|
June 1994
(priorart)
Method to Allow the Sharing of I/O Port Addresses between a Floppy Disk Controller
and an IDE Controller within a PS/2 Micro Channel System
April 1994
(priorart)
Conversion Connector for the IBM Personal Computer
What's
left of information on Intel's Site (archived)
Floppy drive adapter (For Models 50, 60, 70 and 80, by Bob Eager)
60/65/80 - Floppy Drive Variants and Reliability
60/65/80 - Replacing Capacitors
85/95 - Installing a Floppy
Formatting 720K Disk on 1.44MB Floppy
Formatting 360K 3.5" Floppies
System to Floppy Drive List
Floppy Drive to Manufacturer List
PS/2 Floppy Controllers
95A (82077SL) Floppy Controller
Media Formats
Floppy Interface Pinout
2.88 Floppy to Clone Hack Progress
FIFO Mode
Planar Floppy Types (DisketteDrive[x] in Dplanar.ADF)
2.88MB Floppy
Perpendicular Mode
2.88MB Floppy Disk Construction
Gap2 Information
2.88MB Floppy Source (1,000s of them!!!)
* Marked 2.88MB Floppy Drives
Differences Between M356C and M356F
Mitsubishi MF356F-899MF Tape Connector
Function of Third Floppy Connector
Error 165- Is The Floppy Working?
8580 Floppy Drives in the 95?
Disable Floppy Under Setup
OS/2 MCA Floppy ADDs
OS/2 ver 3 and DMF Workaround
Removable Media Security
Secure Media Mode
2.88MB Electronic Eject Floppy
EE Floppy Security Circuitry
Registers
EE Commands (Registers- Lock, Unlock, Eject)
Issue an Enhanced Command
The floppy controller and interface connector reside on the system board.
PS/2 Floppy Controllers
95A Floppy Controller
It is an NEC N82077SL, 68 pin SOIC. It seems Intel bought the chip rights from NEC.
The diskette drive controller supports:
- Four data transfer rates: 250k / 300k / 500k / 1M bits per second
- Programmable precompensation
- A 16-byte FIFO buffer
- PS/2 Style 3.5" 1.44/2.88MB, enhanced 2.88MB, 5.25" 1.2MB
- The secure media mode and the enhanced commands
The 82077SL internally samples the IDENT and MFM pin level which is used to
configure the operating mode (PC-AT, Model 30, PS/2) on the falling edge of H/W reset.
82077AA Removal of DMA Request(DRQ) During an Under/Overrun Condition (archived)
82077 SL Power-on Reset Problem (archived)
82077SL: t23a Timing Clarification (archived) (txt)
Interface Between 82077AA/SL and the Floppy Drive (archived) (txt)
Replacing The 82077SL With The 82078 (44PIN) (archived)
Replacing The 82077SL With 82078 (64PIN) (archived)
Sony MP-F40W - 14/15 There are dash 14 and 15 are two new drives from Sony
that handle 4 MB requirements. The MP-F40W-14 has the DENSITY SELECT 1, DENSITY
SELECT 0 on pins 2 and 33 respectively, whereas the MP-F40W-15 has the DENSITY
SELECT 1, DENSITY SELECT 0 on pins 2 and 6 respectively. As it is obvious from
the table below, daisy chaining is easily done if the 82077AA/SL is connected
in the PS/2 mode (by typing IDENT high) with either type of drive, the only
difference being the location of DENSITY SELECT 0.
95 and 90 Floppy Controller
These systems use the Intel 82077AA floppy controller. The EE floppy drive
can be used on them, but the AA does not support the EE functions.
9577 Bermuda Floppy Controller
These systems use either the 82077AA, 82077SL (rare), or the
NS PC8477AV floppy controller. Usually, systems with the NS controller use
"*" marked floppy drives. BUT I have found some 82077AA/* combinations, plus
what I believe to be a late Bermuda with a 82077SL floppy controller with
a * marked floppy on it...
EHD Capable Controllers and Planars (from David Beem)
Here is the listing of 82077xx FDC chips that are able to support the 2.88
EHD drives:
| Planar | Processor | FDC |
|---|
| 35SX #1 | Intel 386SX-20 | Intel 82077AA |
| 35SX #2 | Intel 386SX-20 | Intel 82077AA |
| 53 486SLC2 | IBM 486SLC2-50 | Intel 82077SL-1 |
| 56SLC | IBM 386SLC-20 | Intel 82077AA |
| 57 486SLC2 | IBM 486SLC2-50 | Intel 82077SL |
| 77 "Bemuda" #1 | Upg. Intel 486DX2-66 | NS PC8477-AV |
| 77 "Bemuda" #2 | Upg. Cyrix 486DX2-75 | Intel 82077AA |
| 77 "Lacuna" | Upg. 83MHz POD | Intel 82077SL |
| Reply 80 | Upg. 83MHz POD | Intel 82077SL |
| 85 (X, K, N) | Intel 486SX-33, DX2-66 | Intel 82077SL (1) |
| 95 (K-M) | Type 1-3 Complex | Intel 82077AA (2) |
| 95 (N-Q) | Type 4 Complex | Intel 82077SL (3) |
Notes:
1) All models support the 3.5" 2.88MB floppy and the EE floppy.
2) Known to support 3.5" 2.88MB floppy (Early 8595s do NOT support the 2.88MB floppy)
3) All N-Q support the 3.5" 2.88MB floppy and the EE floppy.
One pattern seems to emerge from the PS/2 planars: the "souped-up" or
second-gen planars have the 82077SL FDC chips. A couple of surprises though. I
did find two other FDC chips on my equipment. The first on Bermuda planar #1 is
a National Semiconductor 8477AV-2 chip *without* the "(C) NEC 1979", but with
"(C) NSC 1991". Probably a 82077AA replacement that is reverse engineered
enough to avoid having to use the NEC copyright. That system is unchanged from
the way I bought it, with an "*" 2.88 drive. The spare 2.88 I got on eBay I am
unsure of the original model is a non-"*" drive.
There is a smaller surface mount Intel 82091AA in my HP NetServer that does
bear the "(C) NEC'79" & also "(C) Intel '86 '93". Just a guess again about
being a replacement for the 82077AA with the end of the part number. All the
Intel 82077AA and 82077SL chips I have otherwise have "(C) NEC 1979" & "(C)
Intel '86 '91" of course. Other clone motherboards and adapter cards I have
don't look like they have a stand-alone FDC chip. Most support the EHD drives
in the BIOS, so it has to be a variant of the 82077xx somehow (Even the
enhanced NEC 72065B doesn't support 2.88 drives.).
FDC chips are supposed to give which level they are by a "ver" command given
to the chip. By my reference all flavors of the 82077 return the same value. I
have tried a routine for the FDC ver command that so far has *not* worked. The
PS/2 35SX and 53 486SLC2 planars both give a return value for a standard FDC
that doesn't support 2.88 drives, then make the computer unable to read the
drive! Here is the (of all things, BASIC) routine anyway & I am going to
keep trying to get it to work.
OLDVAL = INP(&H3F5)
OUT &H3F5, &H10
FDCVER = INP(&H3F5)
FDC = ""
IF FDCVER = &H80 THEN FDC = "NEC 765, Intel 8272 or compat., no 2.88 support"
IF FDCVER = &H81 THEN FDC = "Intel 82077xx or compat., 2.88 support"
IF FDCVER = &H90 THEN FDC = "NEC 72065B or compat., no 2.88 support"
IF FDC = "" THEN FDC = "Unknown FDC ver value " + HEX$(FDCVER) + "h"
PRINT FDC
OUT &H3F5, OLDVAL
Planar Floppy Types
If you look at the DF9FF.ADF, you will see:
DisketteDrive[1]=2
DisketteDrive[2]=1 2 4
Supported Values (from Tim N. Clarke)
| Value | Meaning |
|---|
| 1 | 5.25", 360 KB |
| 2 | 5.25", 1.2 MB |
| 3 | 3.5", 720 KB |
| 4 | 3.5", 1.44 MB |
| 6 | 3.5", 2.88 MB |
| 7 | Floppy Tape |
This is sometimes useful to add diskette support for a
specific size/capacity.
The point of all this is that I found that the 1.2 MB could be configured
as "Drive B:" by editing the system ADF to add the 5.25" drive codes, provided
that the later version of SC.EXE (V2.20?) was being used.
Formatting 720K Disks on a 1.44MB Floppy
> Why don't you use format /f:720 in the DOS window to make the 1.44 disks
720k suitable? Maybe the 720k machine can't read them later, but this depends
on the drive. 720k drives write wider tracks than 1.44 do.
Peter says:
Guess I jump in here and clear some misunderstandings.
Older PS/2 are non-media sensing - means: whether the floppy has the
right-hand "media type hole" or not doesn't bother these machines. "Klone Chop-Suey-PCs" use to have FDDs that *do* test for
the media type hole - and consequently refuse to read from a down-formatted
1.44MB floppy. You *need* to use a piece of transparency tape around the
front edge and cover the hole from the *underside*. This does not have any
effect on the older PS/2s as explained in 1. above. The "generic" FDDs use
a set of switches on the right side to test for a) floppy presence and b)
presence of a "High Density" hole. (2.88MB drives have a third switch that
tests for "eXtra Density" hole, which sits a bit further away from the lower
edge of the floppy). Some older PS/2 FDDs have the switches too - but they are
used for media presence only - not for detecting the media type, like e.g.
in a Mod. 50/60, 55/65, 70/80 and the 30-286. If you'd closed the media type hole on an actually 1.44MB
formatted floppy and try to format it on a "non PS/2" machine it might complain
on a false format in a first attempt. You better use a PS/2 (see 1. ) On
DOS after 3.x you need to use FORMAT A: /U /F:720 to format to 720KB. On
DOS 3.x you need to use FORMAT A: /N:9 /T:80 to force a 720KB format.
The /U parameter in later DOS (and Win95 DOS box) does an "unconditional"
format and ignores all data and formats on the floppy. It does a *physical*
format across all sectors and actually writes the 720K structures at all. If
you would use the /Q parameter the drive would only try to rewrite the first
sectors with the File Allocation Table (FAT) on that floppy and leave the rest
untouched - that will not work and will result in a media error anyway. The
/N:9 parameter on older DOS is the difference between 720K and 1.44MB format.
Both use 80 tracks (the /T:80 parameter), but 1.44 uses 18 sectors (would be
/N:18), while 720K uses half of them - therefore /N:9.
The *track width* is the same on 720 and 1.44 format - because both use 80
tracks and the stepper motor does the same step-width - and the R/W-head gap
does not change during the process... :-)
Once you have formatted a 1.44MB floppy to 720KB you might be unable to
re-format the floppy back to 720KB - even if you remove the covering tape from
the media type hole. 1.44MB floppies use a Ferro-Chrome (FeCr) base material,
which "holds" the magnetism a bit stronger than the Ferrite-Oxyd (FeO) material
usually used for 720K floppies. The R/W amplifier on generic FDDs might be
unable to fully erase the 720K format in this case.
Formatting 3.5" to 360KB (from Peter)
Old PS/2 that do not care (much) for the floppy formats and
use an older DOS (like Mod. 50/60, 55/65, 70/80 with DOS 3.3 to 5.0) can
be convinced to format a 3.5" floppy to 360KB with using FORMAT A: /N:9 /T:40
... if you then have a machine with a 5.25" drive as well (as on my good
old trusty Mod. 80-A21) you can use DISKCOPY B: A: to make 3.5" copies from
the 5.25" disks onto 3.5".
Interestingly, most machines support 3.5" / 360KB format and can at least
read it.
System to Floppy Drive List
This list does not mean that you cannot use a later drive on
an older system. That is determined by the BIOS of the system. I do not know
the limits of all these models.
EE = Electronic Eject
7568 Floppy Drive
1.44MB 15F7503 (Damn 32 pin tape connector!)
8535/8540 Floppy Drives
1.44 85F0050
2.88 64F4148
2.88 92F0132 (EE) Do these have 82077SL?
8550 Floppy Drives
1.44 64F0207
8555SX Floppy Drives
1.44 64F0162
8556/8557 Floppy Drives
1.44 85F0050
2.88 64F4148
2.88 92F0132
8560, 8565, 8580 Floppy Drives
1.44 64F0162 (Pin Conn. LED below slot)
1.44 72X8523 (Edge Conn. LED above slot)
8570 Floppy Drives
1.44 64F0207
8570/8573 (P70/P75) Floppy Drives
1.44 38F5936
1.44 64F0162 (Not listed, but will also fit, and is electrically compatible.)
8590 Floppy Drives
1.44 64F0162
2.88 64F0204
2.88 64F4148 Not listed, but useable. See Warning below!
2.88 92F0132 (EE) Not listed. Does not have a 82077SL Floppy Ctrl.
8595/9585/9595/9595A Floppy Drives
1.44 64F0162
2.88 64F0204
2.88 64F4148 Not listed, but useable. See Warning below!
9556/9576 and 9557/9577 and i/s
1.44 85F0050
2.88 64F4148
2.88 92F0132 (EE) Bermuda 56/57 planars lack 82077SL. Does not support EE.
Server 500
2.88 82G1888
Floppy
FRU to Manufacturer List
List is NOT complete. Remember that an FRU can refer to many
similar drives.
1.2MB Floppy FRU to Manufacturer
List
64F4102 (Electronic Eject)
Canon MD5501A
1.44MB Floppy FRU vs. Manufacturer
64F0162 (Pin Conn. LED below slot)
Mitsubishi MF355C-599MQ4
ALPS DFP723D30B
15F7503
ALPS DFP723D12F (32 pin tape connector!)
2.88MB FRU vs. Manufacturer
64F0204
Mitsubishi MF365C-799MA
64F4148
Mitsubishi MF356C-799MS
Mitsubishi MF356F-899MF Asterix Marked!
54G1679
ALPS B12HP004113 Possibly Japanese models only (Thanks Sandy)
82F1888
Mitsubishi MF356F-815MB (Uses clone-like short floppy eject
button)
2.88 92F0132 (Electronic Eject)
Sony MP-F40W-07 (also marked MFD-40W-05)
64F0206 vs. 64F4148
From Peter:
These have no grey plastic sled undersides but the metal mounting
plate with integrated side rails. I think that's the major difference between
64F0206 (Peter, don't you mean 64F0204?)
and 64F4148 .. if you look into EPRM you will find that all -4148s are for
35/40, 56/57 and 76/77 - while the -0206 is for the Mod. 85/90/95.
Mounting Hardware
Model 85/90/95 Floppy Drive Slide
64F0156
33F5613
More info about mounting hardware HERE
Mechanics of 2.88
vs 1.44
This was derived from Intel 82077SL for
Super Dense Floppies. The artwork is from this intel document, I just
cleaned them up a bit.
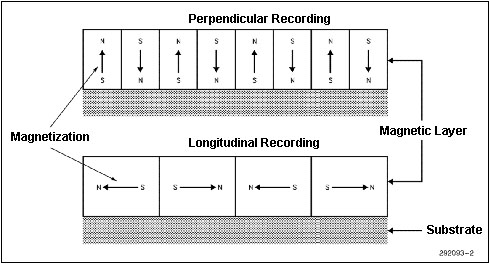
PERPENDICULAR
RECORDING MODE
Toshiba has taken the 2 MB floppy and doubled the storage capacity
by doubling the number of bits per track. Toshiba achieved this by an innovative
magnetic recording mode, called the vertical or the perpendicular recording
mode. This mode utilizes magnetization perpendicular to the recording medium
plane. This is in contrast to the current mode of longitudinal recording which
uses the magnetization parallel to the recording plane. By making the bits
stand vertical as opposed to on their side, recording density is effectively
doubled, Figure 1. The new perpendicular mode of recording not only produces
sharp magnetization transitions necessary at higher recording densities,
but is also more stable.
2.88MB
Floppy Construction
The 4 MB disks utilize barium ferrite coated substrates to achieve
perpendicular mode of magnetization. Current disks use cobalt iron oxide
(Co-g-Fe 2 O 3 ) coating for longitudinal recording. The barium ferrite ensures
good head to medium contact, stable output and durability in terms of long
use. High coercivity is required to attain high recording density for a longitudinal
recording medium (coercivity specification of a disk refers to the magnetic
field strength required to make an accurate record on the disk). A conventional
head could not be used in this case; however, the barium ferrite disk has
low coercivity and the conventional ferrite head can be used.
The new combination heads include a pre-erase mechanism, i.e., the ferrite
ring heads containing erase elements followed by the read/write head. These
erase elements have deep overwrite penetration and ensure complete erasure
for writing new data. The distance between the erase elements and the read/write
head is about 200mm. This distance is important from the floppy disk controller
point of view and will be discussed in later sections.
Gap2 Differences
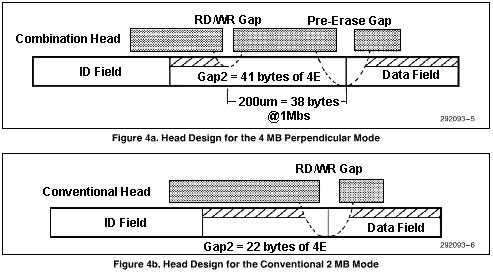
The implementation of 4 MB drives requires understanding the
Gap2 (see Figures 2a and 2b) and VCO timing requirements unique to these
drives. These new requirements are dictated by the design of the "combination
head" in these drives. Rewriting of disks in the 4 MB drives requires a
pre-erase gap to erase the magnetic flux on the disk preceding the writing
by the read/write gap. The read/write gap in the 4 MB drive does not have
sufficient penetration (as shown in Figure 4a) to overwrite the existing
data.
In the conventional drives, the read/write gap had sufficient
depth and could effectively overwrite the older data as depicted in Figure
4b. It must be noted that it is necessary to write the conventional 2 MB media
in the 4 MB drive at 500 Kbps perpendicular mode. This ensures proper erasure
of existing data and reliable write of the new data. The pre-erase gap in
the 4 MB floppy drives is activated only during format and write commands.
Both the pre erase gap and read/write gap are activated at the same time.
As shown in Figure 4a, the pre-erase gap precedes the read/write
gap by 200mm. This distance translated to bytes is about 38 bytes at a data
rate of 1 Mbps and 19 bytes at 500 Kbps. Whenever the read/write gap is enabled
by the Write Gate signal the pre-erase gap is activated at the same time.
2.88MB Floppy source (DEAD)
There is a outfit called WSG Group
(site is under heavy construction) that is a high volume diskette supplier. They
currently have over 600,000 finished, ready to go diskettes, 2DD; 2HD; and 2ED.,
with a back-up of raw materials of over 2 Million diskettes awaiting production...
Resistor Network by 95A Floppy Controller
Bourns 4816P-002 -103 (bussed 10k ohm) (datasheet).
* Marked 2.88MB Floppy Drives
I just noticed that the 2.88 floppy drive in one of my PS/2
machines has an asterisk (*) printed on the top side of the blue eject button.
Anybody has a clue as to what that might indicate? Is it just there for looks?
From Peter:
The drives with the asterisk are those for 35/40, 56/57 and
76/77 - but *not* for 85/90/95. Should be a 64F4148, while the "others" use
a 64F0204. They differ slightly in the pinout and can damage the
planar on earlier Mod. 90 / 95. (Ed. I'm
using an asterisk 2.88 on my 9590. Note:
This is a later planar!)
Hi Al !
>9595 floppy is FRU 64F0204. Floppy I have that is mounted to the sled
is FRU 64F4148. Can I use this floppy on my 9595/8595 without fear?
That 64F4148 is the 35/40, 56/57, 76/77 FDD. If you really like
your 95 you *do not* try it in there. A team mate once did it ... and it
took us some days to solder in a new FDD-controller ... (main problem was
to find one at first)
I cannot figure out *exactly* what caused the mess, but it has
to do with the "security features" available on the 95 - and the corresponding
pins on the 56 - 77 being not present and set to GND. For the older 8595
IBM published a warning, that use of the inappropriate FDD could permanently
damage the planar.
From Us, The god-Emperor of Microchannel (The royal plural)
I whipped out my asterix marked FRU 64F4148. It's a
Mitsubishi MF356F-899MF. I just pulled my stock 2.88 from my Bermuda planar
9577- it is a 64F4148 as well, BUT the Mitsubishi model is MF356C-799MF.
First postulation of the "Law of the Asterix" (you heard it here first, folks!)
is that the MF356F is the model that is incompatible with early 90s/95s.
As noted above, I have used the " * " floppy on a 9590 with no unusual
results. I figure that there must be a more primitive floppy controller used
on the 35/40 etc. systems. I do not have one of these to check.
Differences Between M356C and M356F
From Peter:
BTW: the most obvious difference between Mitsubishi MF356C-799 and
-899 is that -799 has a longer upper cover and the connector on the left
side (looking at the rear), while the -899 has a shorter upper cover and
the connector on the rear right side.
So they differ a lot through the mechanism (different position
of the head actuator stepper motor). For the electronics part - I can't say.
Us, the God Emperor of Microchannel:
With the recent interest in star and non star floppies,
I dug down into my War Reserves and pulled out some
64F4148. At this point, I have three different floppy
drives that wear "FRU 64F4148" and even "ASM 64F5996"
[Non-Star] Mitsubishi MF356C-799MA
[Star "*" ] Mitsubishi MF356F-899MF
[Non-Star] Sony MP-F40W-03
Only the Mitsubishi MF356F-899MF is a Star floppy. No
other floppy drive has a star.
There are three different drives that share "FRU
64F4148", so that is NOT the important part.
Only the Mitsubishi MF356F-899MF has "EJECT" on the PCB
[no components]
My SWAG is the -899MF is a [failed?] Electronic Eject
floppy, akin to the Sony MP-F40W-07.
Mitsubishi MF356F-899MF Tape Connector
64F4148/ ASM 64F5996
This has a 13 pin ribbon cable between the PCB over the
spindle motor PCB and the YG-F1 PCB. One pin is "EJECT"
and there are two solder pads on YG-F1 with the title
"EJECT". Hitachi 3F4
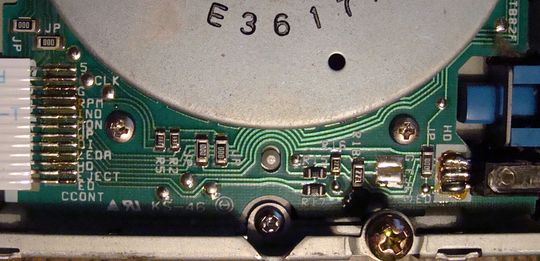
5 +5v
CLK Clock
G Ground
RPM RPM
IND
MON
WP Write Protect
OI [DI?]
LEDA LED "A"
HD High Density
EJECT [missing] Eject
ED CCONT - Extended Density Current Control (i.e. ± signal)

Mitsubishi MF356C-799MA
64F4148 / ASM 64F5996
This has a 9 pin ribbon cable between the PCB over the
spindle motor PCB and the YG-F1 PCB. Mitsubishi M56638FP
ED
HD
G
LED
WP
DI
ID
???
VCC
Third Floppy
Connector Purpose
> I noticed that the diskette drive connects to the motherboard using some
sort of strange connector. It appears to be about 44 pins or so (compared
to the SCSI connector), and the ribbon cable has *3* plugs coming off it.
I never heard of anyone putting 3 diskette drives in a machine
(let alone a PS/2), and diskette drives use 30 (?) pins. So what are
the extra pins and connector for?
From Peter:
The Mod. 56 / 57 / 76 / 77 / 85 / 90 / 95 use a somewhat different
FDD-connector on the planar. They have the Type-3 FDD-interface, which also
supports 2.88MB drives ("Media-Sense Drives"). The third connector is for
a very odd ITBU Internal Tape Backup Unit, which was a slightly modified
IRWIN 120MB tape. The machine supports only 2 FDDs - as usual.
Ed. Configuring The 82077 For Tape Drive
Mode
The FDD-plugs are 34-pins (2 x 17), only the planar connector
is a bit strange 44-pins. This type of interface contains also lines for security
control, i.e. in connection with the "Electronic Eject 2.88MB FDD", which
can be locked and password protected.
Tried to find a pinout of the connector but haven't found any
at the moment ...
System Reports 165-
But Is the Floppy Working?
From Tim Clarke:
>b) the floppy controller/drive/cable is suspect and needs looking at.
However, one would have expected a 601 error is things were really bad.
Peter Responds:
Not always. A dysfunctional FDD may as well cause a 165. "It
is configured - but does not respond". If the heads stuck, do not pass Track-00
tests or have RDATA stuck high or such you will surely get a 600-series error.
But if the drive has a "DC leak" and simply appears as absent it is judged
as "device missing but still present in the configuration".
8580 34
Pin Floppy Drives
From Fred Spencer:
These pin style diskette drives can be sub-divided into two
sub-groups. The original model 8580 drives are identified by the P/N 90X6766.
I have seen these drives labeled as manufactured by Mitsubishi, Alps Electric
and YE Data. Later models were produced for the 8595 and they are identified
by the P/N 72X6112 or 1619618 and also sometimes accompanied by the FRU #
64F0162 , which is also the FRU # reported in the HMM (October 1994) for
both the 8580 and the 8595. HOWEVER, I have discovered that although the
8595 drives (FRU #64F0162) will work on the 8580, the 8580 drives (P/N 90X6766)
will NOT work on the 8595!! The
drives with FRU # 64F0162 have also been labeled as manufactured by Mitsubishi,
Alps Electric and YE Data.
Disabling Floppy under Setup
Even if you use the selectable boot and remove the 1.44, A:
drive from the boot sequence, there is a "safety" device that always looks
at the A: drive for a Reference Diskette. If there is a Reference Diskette
in the drive it will override "selectable boot".
OS/2 Floppy Devices
After the installation of OS/2 Warp and OS/2 Warp Fullpack, CONFIG.SYS
file contains two diskette-driver statements: IBM1FLPY.ADD and IBM2FLPY.ADD.
Only one of the drivers is loaded; the other just takes up disk space. On
MCA machines, you need IBM2FLPY.ADD. You may delete IBM1FLPY.ADD.
Notes: HERE
* IBM1FLPY.ADD with /MCA works on the IBM PS/2 Micro Channel systems.
* If installation is from DMF diskettes, use IBM1FLPY.ADD /MCA for PS/2 MCA systems.
OS/2 Warp with WIN-OS/2 V300
Microsoft has confirmed they have changed their compression utility
for windows products now shipping. The type of compression is not recognized
by OS/2 3.X on some older PS/2's. For example, some model 80, 70 and 65 machines.A
programming error was found but will not be corrected. It is a permanent
restriction..
Local Fix
1. In config.sys
rem basedev=ibm2flpy.add
and use
basedev=ibm1flpy.add /mca
2. If above does not work then use following instead,
BASEDEV=IBM1FLPY.ADD /MCA /A:0 /U:0
/F:1.44MB /CL:AT
Media formats supported
Media
Size |
Capacity |
Sectors
/ Track |
# of Tracks |
Data Rate
(kbit/s) |
| Unformatted |
Formatted |
| 3.5" |
1.0 MB |
720 KB |
9 |
80 |
250 |
| 3.5" |
2.0 MB |
1.44 MB |
18 |
80 |
500 |
| 3.5" |
4.0 MB |
2.88 MB |
36 |
80 |
1000 |
| 5.25" |
0.5 MB |
360 KB |
9 |
40 |
300 / 250 |
| 5.25" |
1.6 MB |
1.20 MB |
15 |
80 |
500 |
Floppy Interface Pinout
The cables pass control and data signals between the diskette drive
controller on the system board and the drives. They also provide the power to
each drive.
Floppy interface pinouts HERE.
2.88 Floppy to Clone Hack
Just when you thought it couldn't be done... This is not a 100%
reliable way to hack the 2.88, BUT it shows that a strong possibility exists.
From Sören Hedlund
Since Febr I've tested with Sony MP-F40W-03 - and still
working on these machines, so I don't believe there is a reliability problem.
Yes, 1.44 disk works fine, but not 720 - you loose about 5% when formatting.
However, I also had to make a circuit to make these Sony MP-F40W-03 to work
properly with all three formats.
Tested MB with IBM 2.88:
Tyan S1572 ATX - SMC fdc37c669qf
p
Aopen AX5T
- SMC fdc37c932apm
QDI TITANIUM 1 - NS9724ax pc87336vlj
Asus PVI-486SP3 - UMC um8669f
Epox MVP3G5 -
Winbond W83877TF
(Hot Shuttle Hot-433 - UMC um8663af -- No 2.88 !)
(Compaq PRESARIO - not in BIOS - No 2.88 !)
So if BIOS support 2.88 it does not mean it will work, the
I/O - chip must support it as well.
From Joseph Realmuto Jr:
The first is a 386-40 with a SIDE4 HP multi-IO
card(2.88MB capable floppy controller). Since this machine does not have
built-in 2.88MB support I had to use a TSR which updates the computer's BIOS.
The floppy controller on the card is capable of 1 Mb/sec data rate.
I connected pins 34, 32, 30, 28, 26, 24, 22, 20, 18, 16, 12, 8, and 2 on the
P/S2 floppy to the corresponding pins on the controller. I left pins
4, 6, 10, and 14 on the floppy unconnected. Pin 3 of the floppy was
connected to +5V and pin 11 to ground. The floppy is a Sony MP-F40W-03
connected as the B drive(the A drive is a standard 1.44 MB). The floppy reads,
writes, and formats 2.88MB media. I can also format 1.44MB media to
2.88MB without drilling an extra hole in it. In fact, all media is
automatically formatted at the drive's native capacity unless forced with
the /F switch. I was not able to get a Mitsubishi MF356F-899MF drive
to work on this machine (pins 26 and 34 seemed to oscillate, and the computer
said there was a seek error).
The second is a Packard Bell Pentium machine with an Intel
Triton chipset and an on- board 2.88MB capable floppy controller. I used the
above Mitsubishi floppy(again as the B drive) and this time simply used an edge
card adapter which connects only the top (even-numbered) pins, and pin 1
(ground). I added +5V on pin 3 by soldering a wire from one of the hard drive
power plugs. Again, this floppy works just as well as the one on the 386
machine. It also seems to automatically format at its native capacity regardless
of which media is actually in the drive unless forced with the /F switch.
It seems that pins 4, 10, and 14 can be left either
connected or unconnected(I recommend leaving unconnected). Pin 6 should
be either connected to pin 6 on the controller (which is an N/C on clone
controllers) or left unconnected. It should never be connected to +12V
even though this is in the pinout for the P/S2 floppy for two reasons:
- +12V is not used at all by the floppy drive
- On some (Sony MP-F40W-15) pin 6 is DENSITY SELECT 0 and putting +12V on a
5V logic line can fry the drive, controller, and possibly even the motherboard.
As a last note, the 1.44MB media seems to work well at 2.88MB.
It formats error-free and seems to hold data with no problem.
I am doing some long-term testing to see if it will retain data. At
this time I do not recommend putting anything important on these media.
Please e-mail me if you know of anybody who has tested this long term.
From David Beem:
As I am building up from the basics I am not having too
much trouble so far. Having learned not to assume on my or anyone's theories
I am slowly gaining information to see if I can pull this off. I pulled out
my Model 35SX, disconnected the 1.44M & connected the spare (non-"*")
2.88 drive. After the expected 16x error I have it configure itself &
I am up and running with a 2.88Mb A: drive on a 386SX-20 computer. Cool.
Even like the guy said on your page that he was able to format a standard
HD disk as EHD with no complaints. Mine differed in that I had to tell it
with the /F:2.88 switch, otherwise it formatted it as 1.44Mb (that was expected,
but not *assumed* on my part).
I am using some pretty cheap bulk floppies too. I don't
know how long the information will last, but it is good to know I can test
the EHD media without having to find the exact diskette out there. The Model
35SX uses a 82077 controller as well. As luck would have it I also have an
ISA Adaptec 1542 SCSI board with an onboard 82077 floppy controller too.
I can cross-check the IBM planars to it too see the pinout changes.
Sony Board
With the 1.44Mb PS/2 floppy drives IBM moved one ground
and one unused pin to put the 5 & 12VDC power on the 34-pin connector.
By my references they seem to have inverted a half-dozen control signals
too, but left them in the same relative position on the connector. Modifying
the Sony board with 3 circuit trace cuts and 3 jumpers to account for the
power connections at least allows the clone to power up. The Motor Enable
signal (one of the ones on the "twist" of the cable) is not inverted, so
it spins the drive up when a read from the floppy is given. The stepper moter
doesn't move though because that is one of the inverted signals.
I am going to see which buffer chip is used to invert the
signals between the Adaptec board and the IBM planars. There is probably a
riser with the correct buffer chip(s) I can assemble to do the task with a
little work. At least at the drive end the connector is pretty much the same.
What I have seen is that at the IBM planar end the Model 35, 40, & 53
have a 40-pin connector and the Model 56, 57, 76, & 77 have a 44-pin
connector. I will figure out the pinouts for those too.
FIFO Mode
The diskette drive controller uses
a FIFO buffer to enhance DMA transfer operations. The FIFO buffer is
used in the data transfer phase only, and its operation is transparent to
programs.
Removable Media Security
The diskette drive controller in
this system supports the optional 2.88MB enhanced diskette drive, which has
a media-security feature. This diskette drive supports Lock, Unlock, and
Eject commands; the Lock command inhibits diskettes from being removed or
inserted. Additionally, if the privileged-access password is set and the
diskette drive is in the boot path, the drive is automatically locked.
FRUs I have seen for the 2.88MB enhanced diskette
drive 92F0132, 92F0129, and I saw 82G1888 mentioned as well.
Secure Media Mode
The secure media mode allows the
diskette drive to receive enhanced commands. These commands provide a means
of controlling access to the media in the diskette drives. Through these
commands, programs can eject a diskette or disable the mechanism, which inhibits
media from being removed or inserted.
To determine whether the mode and commands are supported for a specific drive:
- With the enhanced-command bit set to 1, test the state of the drive type
(1,0) signals by reading the Drive Status register.
Note: For info on enhanced-command bit, refer to System Control
Port C (Hex 007C).
- With the enhanced-command bit set to 0, retest the state of the signals.
If the signals change to a binary 11, the mode and commands are supported for
that drive.
2.88MB Electronic Eject Floppy
|
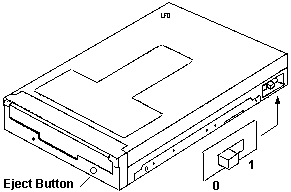
|
0 Eject with eject button or software
1 Eject via software ONLY
|
An optional 2.88 MB diskette drive with security features
is available on some IBM PC Server systems. The diskette drive is a
3.5-inch, one-inch high drive with media sense capability for the standard
diskette capacities of 720 KB, 1.44 MB, and 2.88 MB. It can read and
write data up to a formatted capacity of 2.88 MB, while maintaining read
and write capability with 720 KB and 1.44 MB diskette drives.
A control signal has been added to the diskette interface that
supports LOCK, UNLOCK, and EJECT commands issued by the operating system.
If the privileged-access password is not set, the diskette is unlocked during
POST. If the password is set, the boot process does not unlock the
diskette drive unless it is the designated IPL source. an operating system
utility. For SCSI devices, there is a proposed standard UNLOCK command.
In this case, the operating system will control the LOCK command if the privileged-access
password is set. Access to the unlocking function with specific user
authorization can be controlled by secured system software.
In the event of power loss, the system retains its state (secured
or unsecured) independent of the state of the battery. A diskette can
be inserted in the drive, but it cannot be removed if the power is off.
When the drive is turned on and locked, the media cannot be inserted or removed.
Enhanced
2.88MB Floppy Security Circuitry
>1. Do all floppy controller chips have the
ability to pulse the leading edge of the of the security cmd signal?
No. Only the later machines
support the security functions. It has been offered for the 9595 and 9585
at least. The EE 2.88MB drive comes in two "flavours": 92F0129 for all 9585
and 9595A, 92F0132 for 35/40, 56/57 (all), 76/77 (all)
For the later group I can tell, that
the 35/40 and 8556/8557 have no security features integrated, most likely
the 9556/9557 and "Bermuda" 9576/9577 lack the feature too. The FDD interface
on these machines is a bit different from those on the "Servers". However:
the Server 77i had these security features mentioned in early flyers. So
it appears as if the "Lacuna" machines *have* the appropriate additional
controller logic. (Ed.
The 82077SL FD controller has the extra circuitry that supports
EE)
>2. Is this a hardware function of the controller?
Yes. But requires BIOS support.
>3. Can this be controlled by software (thru BIOS) on any controller?
There was
a tool I cannot recall the name from, which could "lock" the EE-FDD function.
You could neither insert a Floppy when it is empty, nor pull one out if there
is one in the drive. I think they use a logic gate programmed on the controller
to stop the motorized eject / load function.
Tim Clarke
Hi Louis,
I think what the announcement
(and Peter et al.) talked about was software to *cause* the floppy to eject
*not* prevent/disable the feature, although I won't swear to this. I would
think the physical switch is your only option for that. I have the 'electronic
eject' 5.25" slimline floppy in one of my 95s and none of the PC-DOS 7 DRVLOCK
/on, DRVLOCK /off or EJECT utilities accept it (B:) as a supported drive.
And, having thought about it ***there ain't no signal lines to control this
on the floppy interface***. So, perhaps you should get a microswitch and
patch that into the circuit, then mount the microswitch somewhere devious.
Or, even sneakier, figure out if any of the drive select 2/3 or motor enable
2/3 signals are actually passed through the ribbon but not connected on the
floppy drive's PCB circuitry and use one as 'gating control' signal for the
eject signal.
>The *electronic* eject drive is like the
standard push button drive. SONY made both of them. The EE drive
allows you to lock the floppy disk in the drive by flipping the eject button
disable switch on the side of the drive. Unfortantly the program to software
eject the disk via the OS is missing in action ...
The DISKETTE.DGS diagnostics
"overlay" tests the "security features" of the electronic diskette drives
when possible. A bit of reverse engineering might reveal what is needed for
recreation of these utilities. However, doesn't PC-DOS v7/2000 have the DRVLOCK
and EJECT commands? More fodder for the dedicated hacker.
From Peter:
It has - but it fails with the EE-FDD
as far as I can tell. At least when using it in a Lacuna. As far as I can
tell they have been intended for CD-ROMs and MODs. DRVLOCK de-activates the
eject button and EJECT forces a media ject on them. *That* is known to work
under PC-DOS 7.0 with a CD-ROM installed ... I use EJECT recently on my last
PC-DOS survivor.
From Ernst Fueloep:
With OS/2 you can use the security
features for the enhanced 2.88 diskette drive from the diskette icon in the
drives folder. Just press the right mouse button and you will get options
for "Lock disk", "Eject disk" and "Unlock disk".
Make sure the security
switch on the diskette drive is set to 1. You can find this switch on the
right side of the drive.
Electronic Eject Commands
- Lock Drive Disables the load-and-eject mechanism. The
drive will not eject a loaded diskette, nor will it load a diskette. (Depending
on the characteristics of the drive, it may load the diskette and immediately
try to eject it).
Note: Allow 500 ms after an Eject Media
command before issuing Lock Drive cmd.
- Unlock Drive Enables the load-and-eject mechanism, which allows diskettes
to be removed from and inserted into the selected drive.
- Eject Media Same as pressing the eject button on the front of
the drive; it causes the drive to eject a diskette. This command is ignored
if the drive is locked.
Issuing Enhanced Command
Set the value in the data-rate-select bits (in the Data Rate Control register)
at the positive-going edge of the -security cmd signal.
- Select the drive and save the state of the data-rate-select bits.
- Ensure that the System Control Port C is available (bit 7 will be 0).
- Set the enhanced-command bit to 0 (bit 0 of the System Control Port C).
- Set the data-rate-select bits to the desired command.
- Set the enhanced-command bit to 1.
- Restore the data-rate-select bits to the desired data rate.
Note:
If the drive is deselected before the enhanced-command bit
is reset to 1, the drive does not perform the command.
Command encoding of data rate select (1,0)
signals.
Enhanced Commands
Data Rate Select
1 0 |
Resulting
Command |
| 0 0 |
Eject Media |
| 0 1 |
Lock Drive |
| 1 0 |
Unlock Drive |
| 1 1 |
Reserved |
Diskette Drive Registers
| Register |
R/W |
Address |
| Status register A |
R |
03F0 |
| Status register |
R |
03F1 |
| Digital output |
R/W |
03F2 |
| Drive status |
R |
03F3 |
| Controller status |
R |
03F4 |
| Precomp select |
W |
03F4 |
| Command/data |
R/W |
03F5 |
| Digital input |
R |
03F7 |
| Data rate control |
W |
03F7 |
|