|
PS/2 SIMM Memory SYSTEM-BOARD Matrix
For the memory cross-reference table go HERE.
In the case of the 16MB ECC IBM uses the pins 69 & 67 tied against
72 (GND) to recognize it as 16MB / 70 ns ECC... which is accidentally the same
coding as for the 16MB / 70 ns Parity. Unlike to that the ECC SIMM has pin
48 tied to GND as well - the Parity and Non-Parity modules have this pin
not connected.
8MB has pin 69 tied to ground.
Usually the 32MB / 70 ns SIMMs use the PD pattern 70 & 67 open,
68 & 69 closed (GND). The ECC / Non-ECC determination is pin 48 on the
module, which is open on Non-Parity and Parity and GND on ECC modules. So
from the presence-detect part of the story 60 ns modules *could* be reworked.
The problem is the level of integration of the ECC on the module. The "original"
IBM ECC modules are 40-bit modules: 32 (4 x 8) data bits, 4 x 1 ECC bits,
4 x 1 spare bits. The ECC logic is part of the system board. There are different
ECC structures, which use 36-bit memory (parity) and a particular signaling
if the memory integrity is void, there are modules with lesser bits per module
(38 or 39) and modules with "ECC On SIMM" (EOS), which have the ECC logic
on the module and the planar "thinks" they were Parity modules. There is
only a logic signal present that signals a failing module to the planar
logic in case a correctable ECC error occurred. (In case of a non-correctable
ECC error you land on a memory error anyway).
However I don't (yet) know which coding they use. 32MB Parity and 32MB Non-Parity
use 67 & 70 open, 68 & 69 shortened to 72 (GND). Most likely this
same pattern applies to the 32MB ECC as well.
OEM-Memory Modules Specification (by Manufacturer)
| Type |
ID, OEM P/2 |
FRU |
| Kingston |
| 8 MB ECC |
KTM1159 |
|
| 16 MB ECC |
KTM3720 |
|
| 32 MB ECC |
KTM9595 |
|
| Viking |
| 8 MB ECC |
I1159 |
92G7208 |
| 16 MB ECC |
I3720 |
92G7209 |
| 32 MB ECC |
I7210 |
92G7210 |
| 4 MB ? |
I128 |
92G7200 |
| 8 MB ? |
I130 |
92G7203 |
| Mcglen Micro (Viking Components) |
| 16 MB ECC |
DP16I3720 |
|
| 32 MB ECC |
DP32I7210 |
|
| 2 MB ? |
DP2I902 |
|
| 4 MB ? |
DP4I128 |
|
| 8 MB ? |
DP8I130 |
|
| PNY
Has only the Lacuna-76 / -77 in their current list, but the 4/8/16MB modules
from the PS/VP-2 should fit in there. |
| 4 MB / 70 ns P |
P-92G7201 |
(no longer available) |
| 8 MB / 70 ns P |
P-92G7204 |
(no longer available) |
| 16 MB / 70 ns P |
P-92G7204 |
IBM 92G7204 / 60G2950 |
| PIICEON |
| 4 MB / 70 ns P |
907-0345 |
IBM 92G7200 |
| 8MB/70n P |
900-0070 |
IBM 92G7203 |
| 16 MB / 70 ns P |
907-0716 under PS/VP |
IBM 92G7204 / 60G1622 |
| 8 MB ECC |
907-9508 |
2 x IBM 6451158 / 4MB |
| 16 MB ECC |
907-9516 |
2 x IBM 6451159 / 8MB |
| TRANSCEND |
| 2 MB / 70 ns P |
TS2M0902 |
IBM 6540902 |
| 4 MB / 70 ns P |
TS4M0128 |
IBM 6540128 / 92G7200 / 70G9820 |
| 8 MB / 70 ns P |
TS8M0130 |
IBM 6540130 / 92G7203 / 070PS8Y |
| 16 MB / 70 ns P |
|
|
| 8 MB ECC |
TS8M1159 |
IBM 6541159 |
| 16 MB ECC |
TS16M3720 |
IBM 32G3720 |
| 32 MB ECC |
TS32M7210 |
IBM 92G7210 / 070E32Y |
Memory-Presence Determination
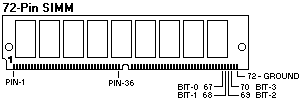
SIMMs that are not clearly labeled cannot be identified
other than by part number.
(For MEMORY component define, you will have the need to know about
70 or more timing/temperature parameters. Because this information will not
fit on a SIMM normally only P/N / Speed and Size is printed on a small Label).
SIMM Identification (Single
Inline Memory Module)
72-pin memory SIMMs are usually marked with a label that shows the size and
speed (e.g. 1Mx32, 60 ns). To determine the SIMM capacity from the
above example, divide 32-bits by 8 (1-byte) and multiply this result by 1M,
hence, SIMM = 4MB (SIMMs prefix -6R = RAS max. 60 ns and Reduced
CAS-timing (-2 ns) appr. CAS = 19 ns)
XMx32 is Non parity and XMx36 is Parity.
PS/2 72-Pin SIMMs (for M/T 85xx/95xx)
A set of 4-bits shows the state of the presence detect signals for a specific
memory connector. The setting of the presence-detect bits is determined through
registers (x'00E8' and x'00E9').
Not all of the following Memory-modules are
supported by every IBM computer.
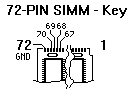
Pin 72 to Pin 70, 69, 68 and 67 ( X = connected to GND)
Presence-Detect Bits Table
Bits.
3 2 1 0 |
Measure
-ment |
Single Inline Memory - Module Definition |
| 1101 |
..X. |
32MB 60-ns Industry standard |
| 1001 |
.XX. |
32MB 70-ns Industry standard |
| 0101 |
X.X. |
32MB 80-ns Industry standard |
| 1110 |
...X |
16MB 60-ns Industry standard |
| 1010 |
.X.X |
16MB 70-ns IBM and Industry standard |
| 0110 |
X..X |
16MB 80-ns Industry standard |
| 1011 |
.X.. |
8MB 70-ns IBM and Industry standard |
| 1000 |
.XXX |
8MB 80-ns IBM and Industry standard |
| 1000 |
.XXX |
4MB 70-ns Industry standard |
| 0100 |
X.XX |
4MB 70-ns IBM |
| 0100 |
X.XX |
4MB 80-ns Industry standard |
| 0000 |
XXXX |
4MB 80-ns IBM |
| 1001 |
.XX. |
2MB 70-ns Industry standard |
| 1100 |
..XX |
2MB 70-ns IBM |
| 0101 |
X.X. |
2MB 80-ns Industry standard |
| 1001 |
.XX. |
2MB 80-ns IBM |
| 0101 |
X.X. |
2MB 85-ns IBM |
| 1110 |
...X |
2MB 100-ns IBM |
| 1010 |
.X.X |
1MB 70-ns Industry standard |
| 0110 |
X..X |
1MB 80-ns Industry standard |
| 0110 |
X..X |
1MB 85-ns IBM |
| 0010 |
XX.X |
1MB 100-ns IBM |
| 1111 |
|
Connector is empty |
|