|
84h7085.exe PC Server 720 reference diskette v1.12 (zipped image)
4227103.exe PC Server 720 diagnostic diskette v1.13 (zipped image)
720pci.exe PC Server 720 PCI Configuration Diskette (zipped files)
4305348.exe PC Server 720 BIOS flash update level 14 v1.10
4305348a.txt README file for BIOS flash update level 14 v1.10
Note: BIOS 10 and diags 1.12 and later properly reset memory cache after testing
720svga.exe PC Server 720 SVGA support diskette v1.01 (CLMODE)
720svga.txt Readme for 720svga.exe
195-071 IBM PC Server 720 with ServerGuide and Related Options
PC Server 720 User's Reference, 1st Ed. (Jul 1995)
720 Planar
Reverse Polarized SMD Capacitor on Video
Buses and Bridges
PC Server 720 Planar FRU P/N 06H1810 (component IDs by Tim Clarke)
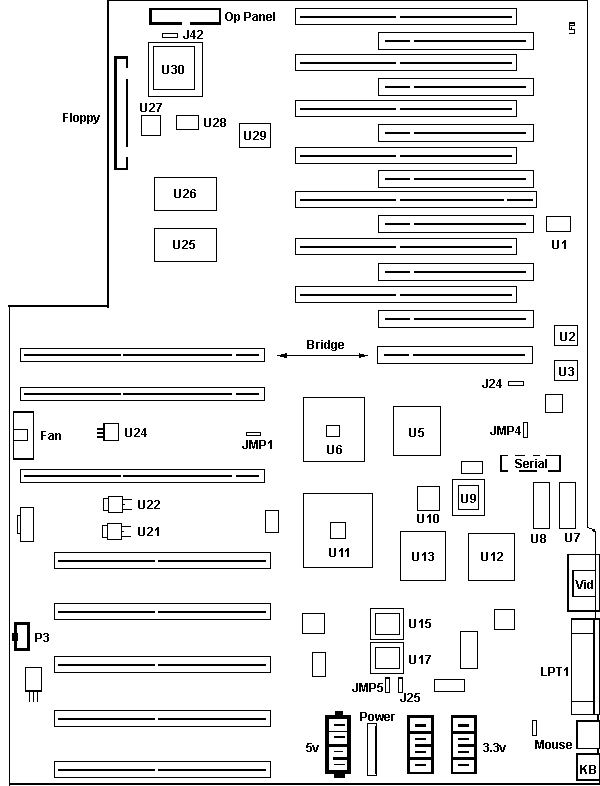
J?? Serial ports header
J24 PCI bus speed select
J25 Remote update (CE use only)
JMP2 Password write-enable
JMP4 Power-on features
JMP5 ROM bank select
U1 14.3181 MHz osc
U2,3 Cypress CY78991-7JC
U4 100 MHz clock for J4 div. selection?
U5 DECchip, D7526C, 21050, VY06867
U6 06H5425 PCI-MCA bridge?
U7,8 NEC 42S4260-70 video RAM
U9 ROM 06H7206 Rev. 1 (video)
U10 06H3195
U11 53G0520
U12 Cirrus Logic CL-GD5429-86QC-C
U13 06H2906
|
U14 06H8922
U15 ROM 75H8834 (system BIOS?)
U16 Sony CX581000AM-70 RAM?
U17 ROM 75H8835 (system BIOS?)
U18 75H0154
U19 40.0000 MHz osc
U20 Cypress CY78991-7JC
U21,22 Power transistors
U23 22.184 MHz osc
U24 Power transistor, well heatsinked
U25 Dallas DS1230Y-70 32Kx8 NVRAM
U26 Dallas DS1587 RTC/CMOS + 8Kx8 NVRAM
U27 82078SL Floppy controller
U28 24.0000 MHz osc
U29 Xilinx XC3042-100 FPGA
U30 (Phillips) 07H0560 Rev. 1
|
U6 06H5425 PCI-MCA bridge? Also used on
the PC 730/750 MCA riser and
the PC 720 riser.
Reverse Polarized Capacitor on Video
Note: (from Tim) The C7 capacitor on the
reverse side of the planar near the video port is the WRONG WAY ROUND, as
with many IBM implementations of the CL-GD542x video controllers. If you
have one of these Server 720s the video output will be dim and will eventually
flicker for a fair while and then finally DIE!!! That's happened to this
planar and is on-going with the one I replaced this one with. BE WARNED!!!
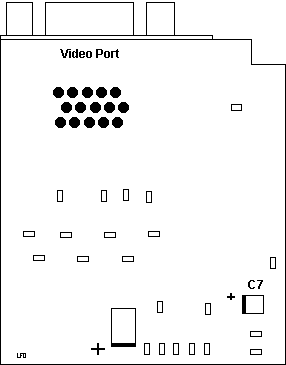
Just like on the Short
1MB SVGA, there is a reversed capacitor on the planar. This is the
original INCORRECT orientation with the positive
side of C7 towards the video port.
Buses and Bridges
(source page 45 phys., edited)
The PC Server 720 incorporates three bus architecture designs.
C-bus II - Multiprocessing Bus
The C-bus II multiprocessing bus is a 64-bit bus that provides symmetric
multiprocessing (SMP) capabilities. It supports up to six processor boards and
has a peak-data-transfer rate of 400 MB/s.
Any processor board connected to the C-bus II multiprocessing bus can be
assigned any application task, and all processor boards connected to this bus
can globally access the system memory and the input/output (I/O) devices in the
server.
The multiprocessor-to-PCI bus bridge connects the C-bus II multiprocessing
bus to the PCI bus. This bus bridge provides a path through which the
microprocessors can directly access PCI devices mapped anywhere in memory or
address spaces.
PCI Bus
The PCI bus is a 32-bit local bus that provides a high-speed data path
between the processor boards and peripheral devices, such as the video and hard
disk subsystems. This bus uses the burst mode for all data transfers. For
32-bit PCI devices, the PCI bus supports a peak-data-transfer rate of 132 MB/s.
It supports PCI bus speeds up to 33 MHz, and allows PCI masters direct access
to system memory.
Expansion slots 1 through 5 are the secondary PCI bus slots. Slots 6 and 7 are
the primary PCI bus slots; you should install your high-performance PCI devices
in these slots. Slot 8 contains the multiprocessor-to-PCI bus bridge.
The PCI bus coexists with the Micro Channel bus, which means that you can
install up to seven PCI, Micro Channel, or a mixture of PCI and Micro Channel
adapters in the expansion slots.
An integrated circuit (chip) on the system board connects the PCI bus to the
Micro Channel bus.
Micro Channel Bus
The Micro Channel bus serves as an expansion bus. Like the PCI bus, the
Micro Channel bus also supports burst data transfers, in which data is sent in
multiple bytes with no intervention by the microprocessor. The Micro Channel
bus also supports streaming-data transfers of up to 80 MB/s.
The Micro Channel bus provides features not implemented in the PCI bus.
These include the streaming-data procedure, channel-check reporting, and error
logging.
|