|
@8DF0.ADF IBM Image Adapter/A (Arb. Level selection, no Int definition!)
@8DF0.ADF IBM Image Adapter/A (Arb. Level fixed, more Mem. choices, Int 2)
@8DF0.ADF IBM Image Adapter/A (no ROM Disable option)
@8DF1.ADF IBM Image and Printer/Scanner Option (Arb. Level selection, no Int definition!)
@8DF1.ADF IBM Image Adapter/A with Printer/Scanner Option (Arb. Level fixed, more Mem. ch., Int 2)
@8DF1.ADF IBM Image Adapter/A with Printer/Scanner Option (no ROM Disable option)
@8DF2.ADF DSS and sub card 2
@8DF3.ADF DSS and sub card 3
@8DF4.ADF IBM Image Adapter/A 3MB
@8DF4.ADF IBM Image Adapter/A (no ROM Disable option<)
@8DF5.ADF IBM Image Adapter/A with Printer/Scanner Option
@8DF5.ADF IBM Image Adapter/A with Printer/Scanner Option (no ROM Disable option)
imageopt.exe PS/2 Image Adapter/A options diskette, version 1.04
Ver 1.02 + correct Arbitration conflict, 1.03 corrects OS/2 2.1 install
iaopt211.exe Image/A & Image-I Opt Dsk (incl 76/77)
Combined I/A and I-I/A, no idea of version, probably later than 1.04?
BIOS version 3.00 14-06-90 ST M27C256B-15 45F3367
The last version seems to be 14/04/92. Unsure if there is a relationship between PCBs?
189-037 IBM PS/2 Image Adapter/A and Related Features
190-108 Image Adapter/A 1MB, 3MB and 3MB 6091
S71G-3708 IBM PS/2 Image / Image-I Adapter/A Technical Reference, 71G3708
S15F-2240 Image Adapter/A Hardware Maintenance Library ('90), 15F2240
S15F-2162 Image Adapter/A Technical Reference ('90), 15F2162
COMPEURO 89 Proceedings VLSI and Computer Peripherals.
May 8 1989 to May 12 1989 Hamburg, West Germany
The IBM Image Adapter/A by R.J. Bowater
A VLSI display controller and processor by Adrian Gay
A 1-micron CMOS 128 MHz video Serialiser, palette, and DAC chip by Martin J Chesters
The VLSI 'silicon compiler' design process by R.M.P. West
Drivers & Software
Image Adapter/A
Image Adapter/A DCP and DSC Functional Islands
Image Adapter/A Versions
Printer/Scanner Option
Image HDD15 Pinout
WIN.INI Options
Displayable Modes
Installing Data Files
Using Non-Standard Displays
Display ID Numbers
Monitors Supported (DISPFILE.0xx)
Incompatible Machines
Known Problems
ADF Sections
Drivers & Software
ia32v211.exe Image/A & Image-I OS/2 Driver (2.1x-BETA)
iadsp211.exe Image/A & Image-I Display Support (required)
ia16v210.exe Image/A & Image-I OS/2 16-bit drivers
iaopt211.exe Image/A & Image-I Option Disk (incl. 76/77)
iawin210.exe Image/A & Image-I Windows 3.x drivers
iados210.exe Image/A & Image-I DOS AI & AutoCAD drivers
Image Adapter/A Versions and FRU P/Ns HERE
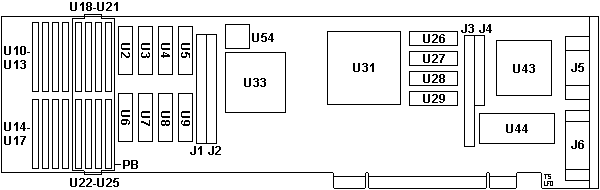
J1-4 Daughercard headers
J5 HDD15 video connector
J6 I/O connector (printer/scanner)
U2-9 256Kx4 DRAM work area
U10-17 512Kx4 ZIPP VRAM (base)
U18-25 Sockets for ZIPP VRAM
U26-29 256Kx4 DRAM Instruction RAM
|
U31 188666 "DSS"
U33 51F1819 "SPD" RAMDAC
U43 1888641 "DS" Display Support Chip
U44 BIOS extension ROM 45F3367
U54 4.0000 MHz osc
PB Bracket for U18-25 (44F9949)
|
U2-9 Micron MT4C4256-8,
TI TMS44C256-12, or compatible 256Kx4 DRAM; Opt. 1 MB Work Area
U10-17 NEC µPD42274V-10,
TI TMS44C256-12N, Samsung KM44C256AP-10,
Micron MT4C4256(Z)-8, or compatible 512Kx4 ZIPP VRAM; Base 1 MB VRAM Display Memory
U18-25 Sockets for ZIPP VRAM (same as above, ≤120 ns); Optional 1 MB VRAM Display Memory
U26-29 TI TMS44C256-12N or compatible 256Kx4 DRAM;
512 KB Instruction RAM
U31 188666 "DSS" RISC Video and I/O Processor chip (Display Controller and Processor (DCP)) "Cotswold II"?
U43 1888641 Display support chip. This *might* be Hitachi HD63484
(datasheet | manual)
Differences Between 07Fxxxx and 06G822x
The '90 07F2511 is littered with decoupling caps... It has a 4.0 MHz crystal
above U33, and a 4.0 MHz osc to the lower left of J1. U33 is 9019 and U31 is
9034. BIOS is 17/10/90. All logic is through-hole but all memory is
through-hole DIPs or socketed DIPs/ZIPs.
The '92 06G8224 (35G4719) only has a 4.00000 MHz osc above U33 and NO XTAL.
The glut of decoupling caps are gone, much smaller SMD logic chips have
replaced more than a third of the logic, but all memory is still through-hole
DIPs or socketed DIPs/ZIPs. U33 is 9226 and U31 is 9223. BIOS is 15/06/92.
The 07Fxxxx versions will positively blow chunks with an M complex. The
06G8224 will work with the M complex...
Huh, I see a 35G4715 / 06G8224, with a DSC of 9106, yet I see other 06G822x
with chip dates of '92... Can't prove it, but this makes sense if the 8221,
8222, and 8223 are the same board but with / without options disk. I wonder if
8224 has the 1.04 options disk...
Installation of IBM PS/2 IA/A in 32-bit system slots is restricted to those
without matched memory extension.
DSC Date Code
DSC chip markings:
| 188641 |
Chip P/N |
| IBM 53 |
Plant Code |
| 02000043100 |
Date / S/N? |
| 05 25 |
Unknown |
The first digit is the year digit starting in 1990. The second and third
digits are the week. So, "020" Means 1990, 20th week.
Image /A Block Diagram
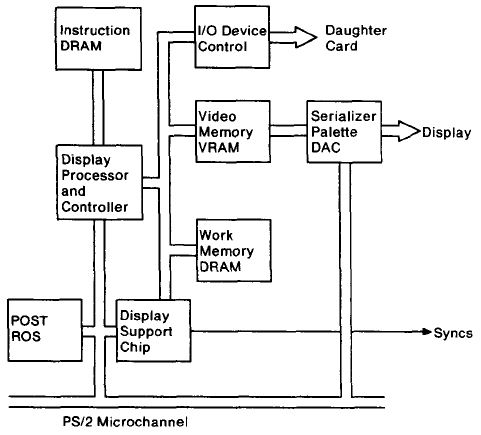
The Display Support Chip A small gate-array VLSI chip providing
synchronization and timing pulse generation for the display and Image Adapter
card.
Image Adapter/A DCP and DSC Functional Islands
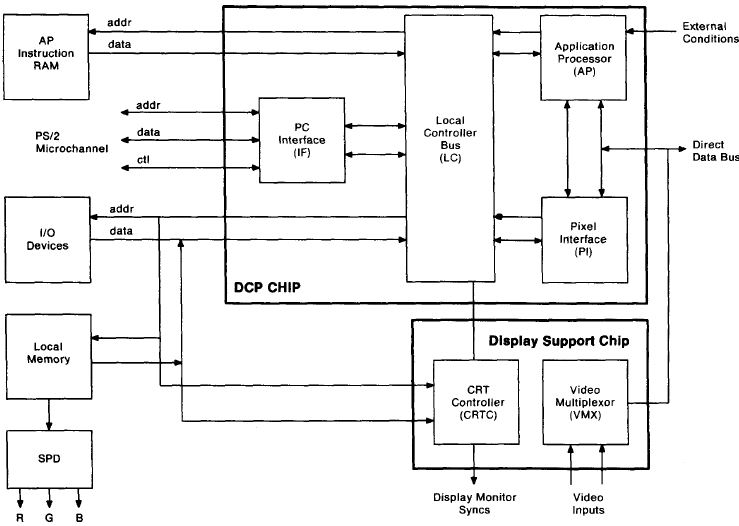
Image /A Display Processor Block
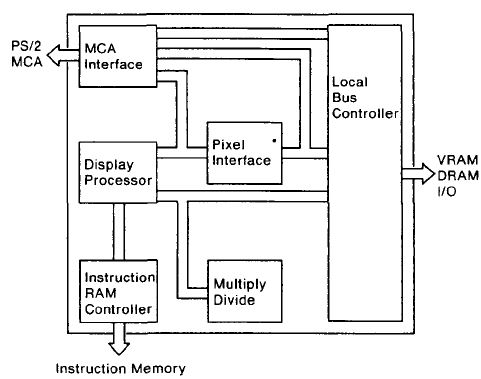
Image/A Serializer / Palette / DAC Block (SPD)
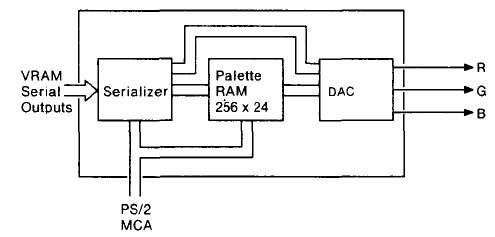
The Serializer/Palette/DAC circuit types integrated on a single chip:
- High speed static RAM (8 ns access)
- Logic (6000 cells)
- Digital-to-Analogue convertors, custom designed
- Phase-Locked-Loop and Voltage-Controlled-Oscillators
The SPD chip provides all the function of the
INMOS G171 component used on PS/2
planars and in the IBM 8514/A display adapter.
However, the SPD has improved flexibility and function over the IBM VGA and
8514A:
- INMOS G171 compatible palette & DAC
- Colour comparators for diagnostic verification of DAC outputs
- 32 bit to 8 bit serializer
- Cost-reduced DAC current and comparator voltage reference sources
- Clocks and dividers for PS/2 monitors of 25.175, 28.321 & 44.90 MHz.
Additional function and flexibility is provided:
- 256 by 24 palette with 8 bit DACs
- Support for a video data word width of 8, 16 and 32 bits formatted as 1 , 2, 4, 8 and 16 bpp.
- Generation of video logic and shift clocks for the CRTC and video RAM
- Differential current outputs.
From what little I see, 16 bpp is "palette bypass" ("Direct Color") like the
original XGA.
Image Adapter/A Versions
- Image Adapter/A 1MB - 1MB VRAM, FRU P/N 06G8221
- Image Adapter/A 3MB - 2MB VRAM and 1MB DRAM, FRU P/N 06G8222
- Image Adapter/A 3MB 6091 - Image Adapter/A 3MB w/ cable for IBM 6091-019.
Note: There is no 2 MB version of the Image Adapter/A.
2 MB VRAM / 0MB DRAM *or* 1 MB VRAM / 1 MB DRAM?
Downlevel (same PCB, different memory amounts)
- P/N 07F4401 - Replaced by P/N 07F2508
- P/N 07F2481 - Replaced by P/N 06G8224 + P/N 75X5894 (8 VRAMs)
- P/N 07F2508 - Replaced by P/N 06G8221
Current (same PCB, different memory amounts)
- P/N 06G8224 - Image Adapter/A 1MB (current)
- P/N 06G8221 - Same as P/N 06G8223 w/o Option Disk v1.03
- P/N 06G8221 - Replaced by 06G8223
- P/N 06G8223 - Replaced by 06G8224 w/ Option Disk v1.03
Printer/Scanner Daughtercard
FRU P/N 07F4403 (from William Walsh HERE)
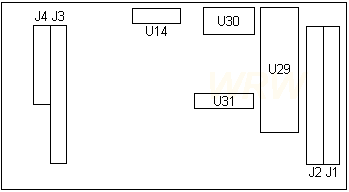
J1-4 Header to base board
U14 75X8841
U29 Zilog Z85C3010PSC SCC
|
U30 10.00 MHz osc
U31 37F9937
|
U29
Zilog Z85C3010PSC SCC (Serial Communications
Controller) 10 MHz
85C30 Optimized for non-Multiplexed Bus Microprocessors
Using Image Adapter/A with 4216-020 Personal Page Printer (from Peter)
FWIW, I was told once by a Lexmark rep that you could also talk to this
printer through a port on the Image Adapter/A card. I never had an IA/A myself,
so I'm not sure if this meant all IA/A's or a certain version or possibly a
special daughtercard.
- This is only applicable for the "Image Adapter /A" - not the Image-I
Adapter.
- You need the "Printer / Scanner Feature Card" FRU P/N 07F4403 and the
"Printer / Scanner Y-Cable" FRU P/N 07F4417. Probably the "Memory Module DRAM"
(Kit) 07F44407.
The Y-cable connects to the IBM 3117 Scanner on the one side and to the
4216-020 "Raw Engine" on the other port. However: the driver support was rather
poor (Win 3.0 / 3.1 and OS/2 up to 2.0 only IIRC). Have seen this combo at a
customer once (back in 1991 or so) but never worked with it nor serviced
it.
Image Adapter/A Part Numbers
1-MB MKT P/N 35G4715
3-MB MKT P/N 35G4716
3-MB + 6091-Cable MKT P/N 35G4717
9527 Cable MKT P/N 95G9906
9521 Cable MKT P/N 95G9907
The Image Adapter/A is capable of driving displays up to 128 MHz, with a
maximum resolution of 1600x1200 pels. The Driver output impedance for video
signals is 75 ohms. The sync lines of the adapter are TTL levels driven by 4ma
drivers, so termination should be at 750 ohms (minimum)
It contains a 32 bit 8.5 MIP display processor, a 128 MHz serializer, video
palette, digital to analog converters and a CRT controller.
Memory consists of 1MB VRAM (U10-17), optional 1MB of VRAM (U18-25), 512KB
of instruction RAM (U26-29) and 1MB DRAM Memory Expansion (U2-9).
Image Adapter/A Options
You can attach optional features only to the Image Adapter/A
- Printer/Scanner Option
- Memory Expansion Kit
- PS/2 Video Memory Expansion Option
For a single display configuration, you must always attach the display to
the display connector on the Image Adapter/A and not to the system unit display
connector.
Image Adapter/A Memory Configurations
| Card |
VRAM 1 |
VRAM 2 |
DRAM 1 |
| 1MB |
8x |
0x |
0x |
| 2MB |
8x |
0x |
8x |
| 3MB |
8x |
8x |
8x |
| 3MB 6091 |
8x |
8x |
8x |
| *Includes cable for IBM 6019-019 Color Display |
Image Adapter/A Memory Modules
FRU P/N QTY DESCRIPTION COMMENTS
07F4407 1 DRAM 128K EACH (8x needed)
75X5894 * 1 VRAM 128K EACH (8x needed)
75X5894 used in XGA Adapter/A, Model 90 planar XGA, and Image Adapter/A.
The three versions of the Image Adapter/A support IBM analog displays
equipped with a 15-pin direct-drive analog interface.
Printer/Scanner Option (#1632)
Allows direct attachment of:
- IBM 3812 Printer Model 002 with Image Feature (#4050)
- IBM 4216 Personal Pageprinter Model 020
- IBM 3117 Scanner with extension unit (P/N 6456808)
- IBM 3118 Scanner or Bell & Howell 2115I (1) Scanner or equivalent
Image Adapter/A enables both a scanner and a printer to be attached at one
time via this optional printer/scanner daughter card. Use of the
Printer/Scanner Option does not require an extra system unit slot.
6019-019 Display Cable
This cable is included with the Image
Adapter/A 3MB 6019. The cable must be ordered separately
for all others.
Image Adapter/A 15-pin Analog Video Connector
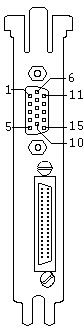
|
| Pin |
Color Mode |
Mono Mode |
| 1 |
Red Video |
Reserved |
| 2 |
Green Video |
Video |
| 3 |
Blue Video |
Reserved |
| 4 |
Display ID 2 |
Display ID 2 |
| 5 |
Self-Test |
Self-Test |
| 6 |
Red Ground |
Reserved |
| 7 |
Green Ground |
Video Ground |
| 8 |
Blue Ground |
Reserved |
| 9 |
+12 V (fused) |
+12 V (fused) |
| 10 |
Digital Ground |
Digital Ground |
| 11 |
Display ID 0 |
Display ID 0 |
| 12 |
Display ID 1 |
Display ID 1 |
| 13 |
External Hsync |
External Hsync |
| 14 |
External Vsync |
External Vsync |
| 15 |
Display ID 3 |
Display ID 3 |
|
WIN.INI Options
An example set of options in the WIN.INI file looks like:
[Image Adapter/A]
Version=2.2
Resolution=1024 768
BitsPerPixel=8
PaletteManager=Yes
MemoryUsage=Maximum
DualScreen=No
StretchBlt=Yes
VirtualScreen=No
You can modify these options by running the IASETUP.EXE program.
Version Version of Image Adapter/A
Win3.1 Display Driver.
Resolution X and Y dimensions (in
pixels) of the display mode required. See HERE for a list of valid modes. If an
invalid mode is specified, the driver reverts to its default (the highest
resolution available on the display attached).
BitsPerPixel Specified as 1, 2, 4, 8 or
16. Note that some of the higher bits per pixel are invalid in some of the
Image Adapter/A memory configurations. If an invalid bits per pixel is
specified, the driver reverts to its default (the highest bits per pixel
available (up to 8) at the selected resolution).
PaletteManager At 1, 2 and 4 bits per
pixel, the palette is fixed to 2, 4, and 16 colors respectively. The Palette
Manager options do not apply and are ignored. Dithering is enabled to
approximate colors that are not in the palette. At 16 bits per pixel, the
adapter is in direct color mode and there is no palette, the Palette Manager
options do not apply and are ignored. Dithering is disabled.
Three PaletteManager options,
at 8 bits per pixel
YES - Palette Manager enabled
At 8 bits per pixel (256 color mode) only 20 system colors are
assigned (10 at the bottom and 10 at the top). The remaining 236 colors are
available for the Palette Manager to assign to applications that request them.
For applications that do not use the Palette Manager, dithering is enabled to
approximate colors that are not in the system palette. This is the default
setting at 8 bits per pixel.
NO - Palette Manager disabled
At 8 bits per pixel the palette is fixed to a particular set of
colors. Dithering is disabled, the driver selects the nearest color available
from the fixed palette.
GRAY - Gray scale palette
At 8 bits per pixel there are 256 shades of gray (even on a color
display). In all other aspects it is like the fixed palette. This option may be
useful for certain applications. This is NOT usually the best palette to select
for monochrome displays, unless the application is specifically designed for
gray level displays.
If you need to switch this option on or off see "Switching the Palette
Manager On and Off".
MemoryUsage Reserved for special
applications designed to run only on the Image Adapter/A. Unless you are using
one of these special applications this option should always be set to
Maximum.
DualScreen Only applies when you have
two displays attached to your system. For example, a VGA display attached to
the standard VGA port of the system unit and a high resolution display attached
to the Image Adapter/A.
NO The display attached to the Image Adapter/A will always be used as
the main display for running Windows applications and full screen VGA
applications. When running full screen VGA applications both displays will be
showing the same results. This is the default setting.
YES During a Windows session the display attached to the Image
Adapter/A will be used only for running Windows applications. When running full
screen VGA applications (from within the Windows environment) only the VGA
display will display the VGA application. Windows applications running in the
background on the Windows display will continue to be updated.
If you have only one display (attached to the Image Adapter/A), select NO
for this option.
StretchBlt Whether the driver registers
its capability to scale images.
YES The display driver will register the StretchBlt capability and
image scaling will be preformed by the adapter. This results in a considerable
performance improvement. This is the default.
NO The display driver doesn't register the StretchBlt capability and
the Windows graphics engine simulates the image scaling in software.
VirtualScreen X and Y dimensions(in
pixels) of the virtual display mode required. The x possible value is 1024,
2048, 4096 and y possible value is 1024, 2048, 3072, 4096. See Table 5, 6, 7
for a list of valid modes. Virtual screen is not supported with only 1MB card.
If invalid value is specified, virtual screen is disabled. If you want to
disable virtual screen, specify "VirtualScreen=No".
Display Modes The following tables show
the display resolutions and bits per pixel available for the various display
and memory configurations. The numbers represent the bits per pixel. A blank
box means the resolution is not supported. There is more information, in the
READ.ME of Display support diskette. Refer it for the detail.
Displayable Modes
Monitor Resolution Max. H-Freq V-Freq Pix-Freq Int
bpp (KHz) (Hz) (MHz)
8503 640x480 16* 31.56 60.12 25.25 N
8504
8512
8513
8518
8514 640x480 16* 31.56 60.12 25.25 N
8515 1024x768 16* 35.60 43.58 45.00 Y
8604
8507
8508 640x480 8 70.79 67.04 64.00 N
1024x768 8 72.33 85.49 103.00 N
1360x1024 8 70.80 67.04 128.00 N
1600x1200 4 62.01 49.33 127.00 Y
8506 864x1200 8 50.57 40.10 53.00 Y
6091-019 640x480 16* 70.75 67.00 60.00 N
1024x768 8 70.75 67.00 120.00 N
1280x1024 8 70.75 67.00 120.00 N
6091-019 640x480 16* 63.06 60.00 55.00 N
(Mode 2) 1024x768 8 63.06 60.00 111.00 N
6091-023 1280x1024 8 63.06 60.00 111.00 N
5081
8517 640x480 16* 31.56 60.12 25.25 N
1024x768 8 56.28 70.00 77.00 N
1280x1024 8 56.46 51.47 103.00 Y
1360x1024 8 56.46 51.47 103.00 Y
1091-051 640x480 I 8 75.47 71.20 64.00 N
1024x768 I 8 75.82 71.53 128.00 N
1280x1024 I 8 75.82 71.53 128.00 N
6091-016 640x480 8 81.14 76.83 74.00 N
6091-19i 1024x768 I 8 81.14 76.83 148.00 N
1280x1024 I 8 81.14 76.83 148.00 N
9515 640x480 16* 39.37 75.00 31.50 N
1024x768 8 61.08 75.78 86.00 N
9518 640x480 16* 39.37 75.00 31.50 N
9517 640x480 16* 39.37 75.00 31.50 N
1024x768 8 58.14 72.04 80.00 N
1280x1024 8 58.11 52.97 106.00 Y
1360x1024 8 58.11 52.97 106.00 Y
* Windows up to 16 bpp, PM/DOS/AIX supports up to 8 bpp
If there is less than 3 MB of memory on Image Adapter/A, displayable modes
and bpp may be reduced.
Image Adapter/A (3 MB) Display Modes
|
8513 |
8514 |
8506 |
8508 |
6091 |
| 640x480 |
1,2,4,8,16 |
1,2,4,8,16 |
|
1,2,4,8 |
1,2,4,8,16 |
| 1024x768 |
|
1,2,4,8,16 |
|
1,2,4,8 |
1,2,4,8 |
| 864x1200 |
|
|
1,2,4,8 |
|
|
| 1280x1024 |
|
|
|
|
1,2,4,8 |
| 1360x1024 |
|
|
|
1,2,4,8 |
|
| 1600x1200 |
|
|
|
1,2,4 |
|
8513 column also refers to 8503 and 8512, and
8514 column also refers to 8507, 8515 and 8604
Direct Color Mode (16 bits per pixel)
Some apps do not cope correctly with 16 bpp, a common symptom is that the
application will think that its running on a b/w device and display as gray
shades. Many of these apps run correctly if the BitsPerPixel option is set to
15. The driver still runs at 16bpp but it informs apps that there are 32,767
colours available instead of the correct value for direct colour devices which
is -1.
How to Install Display Data Files to Your System
Image Adapter/A version 2.00 or later drivers automatically detect the
attached monitor and find correct Display Data File. You can also specify the
name of Display Display Data File to be used and its directory.
Each driver expects the default directory path to find Display Data File if
no special path is specified. The default directories are as follows.
DOS AI: C:\IMGAIDOS
Windows: C:\IBMIAA
OS/2: C:\OS2\IBMIAA (C: is the boot drive here)
AIX: /usr/lpp/ibm-iaa/lpp.ddf
If you wish to specify Display Data File name, please add the option to your
system CONFIG.SYS driver statement like the following example. (The case of
Windows driver)
DEVICE=C:\IBMIAA\IADOSRFS.SYS /DisplayID=49C
Where, 49 is decimal value of hex 31 (DISPFILE.031), and 'C' indicates this
is a color monitor. If you change 'C' to 'M', driver assumes the attached
monitor is a monochrome monitor which has the same timing.
If you wish to change Display Data File directory other than default, please
add the option like the following example. (The case of OS/2 driver)
DEVICE=C:\OS2\IBMIAA\IAOS2RFS.SYS /DisplayPath=E:\DDFPATH
You cannot change default Display Data File path in AIX driver by this
option. Please refer to readme file in each driver diskette for further
information about each driver installation.
Using Non-Standard Displays
The Image Adapter/A can connect to any display that is compatible with the
IBM Displays, 8503, 8506, 8507, 8508, 8512, 8513, 8514, 8515 and 6091 19". To
enable other displays to operate correctly you may need to override the display
ID that is returned by the display.
The display ID override is a command line option that should be placed after
the DEVICE=IADOSRFS.SYS line in your CONFIG.SYS. For example to override the
display ID to 8 for a color display the line would look like:
DEVICE = C:\IBMIAA\IADOSRFS.SYS /DisplayID=8C
Table 9 lists the different ID's that should be used for the various
possible modes. Note that you still need to specify the correct resolution in
the WIN.INI file.
Display ID Numbers
| Screen |
Color |
Mono |
| 640x480 NI |
1 |
2 |
| 1024x768 IL |
5 |
6 |
| 1024x768 NI |
21C |
21M |
| 864x1200 IL |
10C |
10M |
| 1280x1024 NI |
11C |
11M |
| 1360x1024 IL |
21C |
21M |
| 1360x1024 NI |
8C |
8M |
| 1600x1200 IL |
8C |
8M |
Note: IL indicates interlaced modes and NI
non-interlaced modes.
Monitors Supported
Image Adapter/A and Image-I Adapter/A Display Support diskette 2.10.
These files are used to install version 2.00 or later level of Image
Adapter/A and device drivers to your system. Each file has a information table
for the following monitor.
DISPFILE.000 : No monitor
DISPFILE.001 : 8512 8513 8518
DISPFILE.002 : 8503 8504
DISPFILE.004 : 8515 8516
DISPFILE.005 : 8514
DISPFILE.006 : 8604 8507
DISPFILE.008 : 8508
DISPFILE.00A : 8506
DISPFILE.00B : 6091-019
DISPFILE.20B : 6091-019 (Mode 2 60Hz) 6091-023 5081
DISPFILE.015 : 8517
DISPFILE.018 : 1091-051
DISPFILE.019 : 6091-016
DISPFILE.01B : 6091-19i
DISPFILE.020 : 9515
DISPFILE.021 : 9518
DISPFILE.031 : 9517
DISPFILE.080 : 9527
DISPFILE.081 : 9521
DISPFILE.08A : 9504
Painful Probulation (from WBST)
I've been delving into the registers used by the DOS Adapter Interface
device driver for these variants (IDs 8DF0-8DF5, possibly including 8DF6-8DFF
from the code).
Initial comments:
Driver chains Int 7Fh
Support for up to 4 adapters at the same time
Driver uses Int 15h AH=C4h, AL=00h-02h calls to query and enable adapters
Multi-Card Adapter
US5530887A Methods and apparatus
for providing automatic hardware device identification in computer systems that
include multi-card adapters and/or multi-card planar complexes.
The Image Adapter/A is a Multi-Card Adapter:
@8DF0.ADF - IBM Image Adapter/A
@8DF1.ADF - IBM Image/A and Printer/Scanner Option
@8DF2.ADF - DSS and sub card 2
@8DF3.ADF - DSS and sub card 3
@8DF4.ADF - IBM Image Adapter/A 3MB
@8DF5.ADF - IBM Image/A with Printer/Scanner Option
Incompatible Machines
There seems to be three incompatible systems:
- 8557SX (DMA limitation?)
- 8573 P70 (the video slot steals a line for dimming the plasma; see note below)
- 8570-A21 (unknown if the 486 based -Bxx is also affected)
Josh Rodd said:
You can actually use an Image Adapter/A in a P70 if you are
willing to take a dremel tool, knife, etc. to cut off the AVE tab. Then you can
put it into the P70's full length 32-bit MME slot.
You can also jam it into the 16-bit standard slot, with the AVE tab hanging
loose. It's a (very) tight squeeze where the IA/A's RAM is - the card will flex
quite a bit. I had the 3MB version plus the Print/Scan option (with no printer
nor scanner to use it with) and removing this option helped it fit a bit
better.
I ran this set up back in the 1993 - 1994 era, with a dual monitor setup: an
8514 plugged into the IA/A and an 8512 plugged into the onboard VGA. Worked
fine. Nonetheless, the IA/A's official documentation says it is incompatible
with the 8573 P70 machines.
Known Problems
8590/95 "M" System Hang with Image Adapter/A installed (H101665)
A CP 40 (Stage 1 Video Test) POST Hang Condition Will Happen on an 8590 /
8595 0MF or 0MT (50 MHz complex) if an early version Image Adapter/A is
installed.
8590 / 8590 "M" class systems must have Image Adapter/A FRU P/N 06G8224
(MKTing Option 35G4712, 35G4713, or 35G4714). The Following Image Adapter/A
will not work in the 50 MHz 8590 and 8595 FRU P/N 06G8221, 06G8223, 07F2481 and
07F2508.
AdapterID 08DF4h "IBM Image Adapter/A" (with 3MB)
DMA Arbitration Level
DMA channel arbitration level used. The
default of 5 is an arbitrary decision!
<"Level
5">, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 0, 1, 2, 3, 4
Fairness On/Off
Whether IA/A will release control of the
bus when it has been using it exclusively.
<"On">, Off
Adapter I/O Addressing
Adapter I/O Addressing locations
<"I/O Addresses 1D00 to 1D7F">,
2D00 to 2D7F, 3D00 to 3D7F, 4D00 to 4D7F
Adapter Memory Location
Memory location IA/A will use for the BIOS
ROM, and RAM window
<"Segment C000"> (C000-C1FF),
C200 (C200-C3FF), C400 (C400-C5FF), C600 (C600-C7FF),
C800 (C800-C9FF), CA00 (CA00-CBFF), CC00 (CC00-CDFF),
CE00 (CE00-CFFF), D000 (D000-D1FF), D200 (D200-D3FF),
D400 (D400-D5FF), D600 (D600-D7FF), D800 (D800-D9FF),
DA00 (DA00-DBFF), DC00 (DC00-DDFF), DE00
(DE00-DFFF)
Extended Memory Window
Some apps may require an Extended Memory
Window into IA/A RAM to appear high in system address
space.
<"Disabled">, "1 Meg at
Address E00000" (e000-eFFF), D00000 (d000-dFFF), C00000
(c000-cFFF), B00000 (b000-bFFF), A0000 (a000-aFFF),
900000 (9000-9FFF), 800000, 8000-8FFF), 700000
(7000-7FFF), 600000 (6000-6FFF), 500000 (5000-5FFF),
400000 (4000-4FFF), 300000 (3000-3FFF), 200000
(2000-2FFF), 100000 (1000-1FFF)
"2 Meg at Address
D00000" (d000-eFFF), C00000 (c000-dFFF), B00000
(b000-cFFF), A00000 (a000-bFFF), 900000 (9000-aFFF),
800000 (8000-9FFF), 700000 (7000-8FFF), 600000
(6000h-7FFF), 500000 (5000-6FFF), 400000 (4000-05FFF),
300000 (3000-4FFF), 200000 (2000-3FFF), 100000
(1000-2FFF)
Note: WBST
cautions: Extended Memory window can only be enabled if,
at most <=14MB is installed in the system. A slightly
important caveat. This becomes a concern in later
systems.
Interrupt Level
The Interrupt level is fixed at 2
< "Interrupt 2">
|