|
Slot Pinouts
Introduction
MCA Slot Types
Matched-Memory Extension (MME)
Auxiliary Video Extension (AVE)
Base Video Extension (BVE)
Based on content by Peter Wendt (original). Edited and drawings created by Tomáš Slavotínek.
Introduction
The Micro Channel Architecture can be rather confusing on a first glance as
there are multiple different slot variants. We can divide them to two main
groups by the data bus width - to 16-bit and 32-bit slots. Apart from this
there are also 3 special bus extensions - BVE, AVE and MME.
Below you will find illustrations of the various slot types and information
on what purpose the optional extensions serve.
MCA Slot Types
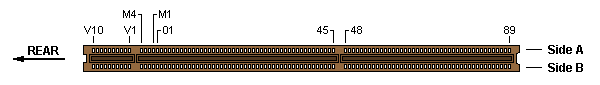
The "component side" (A) and "solder side" (B) refers to an installed adapter card.
The "Rear" arrow points towards the back side of the planar/system unit.
The physical key between pins 45 and 48 serves as a reference point for all connector types.
16-bit MCA slot — Burndy Computerbus CEE2X56S-3Z14 or AMP 650093-1
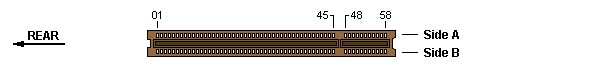
16-bit MCA slot w/ AVE — Burndy Computerbus CEE2X66S-3Z14 or AMP 650094-1
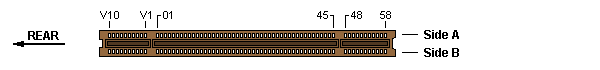
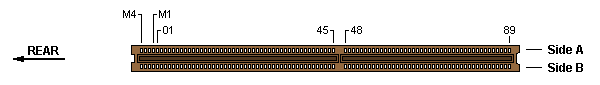
32-bit MCA slot w/ MME — Burndy Computerbus CEE2X91S-11Z14 or AMP 650722-1
32-bit MCA slot w/ AVE — Burndy Computerbus CEE2X97S-12Z14 or AMP 650723-1
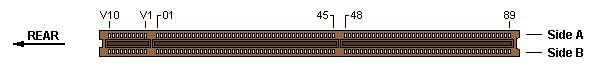
32-bit MCA slot w/ MME & BVE — Burndy Computerbus CEE2X101S-12Z14 or AMP 650724-1
32-bit MCA slot w/o extensions — not used
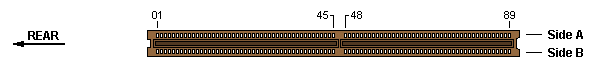
Note: None of the known MCA systems use the 32-bit
connector in its base form. Usually, it includes at least the MME extension,
even in systems that do not support channel memory.
Connector Documentation
Burndy CEE2X drawing SE95508 (CEE2X___S_-V__Z14) (1 sheet - incomplete)
Burndy CEE2X drawing SE93334 (CEE2X___S-V_Z__) (5 sheets)
Burndy CEE2X drawing BRSE96060 (CEE2X__S-V_Z48W) (6 sheets)
Other Buses
The base 16-bit MCA connector was reused by the VESA Local Bus
(1992). The 32-bit variant of the PCI bus (1993) uses a similar 1.27 mm
pitch connector with four additional contact pairs.
Matched Memory Extension (MME)
The MME part of the MCA connector consists of 8 pins (2 x 4) at the rear end
of a 32-bit MCA connector. There is no separation between the base 32-bit
connector and the MME part.
The MME part is used from 32-bit Memory Expansion adapters, which support
Matched Memory Cycles. This can improve the data transfer capabilities between
the system master and channel-resident memory (means: between planar memory and
that on expansion cards).
The use of MME is system-dependent and varies between the different PS/2
machines. Models 70 and 80 support MME - and therefore can be upgraded with
32-bit memory expansion cards. Many later PS/2 systems including the Models 90
and 95 do not support MME and should be upgraded only with memory on the planar
(the Type 0 complex is an exception).
Auxiliary Video Extension (AVE)
The AVE part of the MCA connector consists of 20 pins (2 x 10) at the rear
end of the MCA connector, separated by a key (notch in the card's
connector).
The AVE is intended for cards that don't have their own base-video system -
like the IBM 8514/A Display Adapter /A.
Such adapters can utilize the planar video system through this extension. In
this configuration, the base video modes are handled by the onboard VGA or XGA
subsystem, and the video information is passed through this extension to the
8514/A monitor port. This means that the expansion adapters don't need to
reimplement the base video functionality and the user doesn't need to switch
between the two video connectors or use two monitors.
Other additional video cards that *do not* use the AVE cannot display the
VGA text/graphic mode on the same screen along with their native modes.
They need a second monitor attached to the onboard VGA / XGA card.
In a way, this AVE is the MCA's Video Feature Connector. Cards can use the
onboard video system and for example synchronize their output to the onboard
video.
See the Auxiliary Video Extension
page for more information.
Base Video Extension (BVE)
The BVE part of the MCA connector consists of 20 pins (2 x 10) at the rear
end of a 32-bit MCA connector and after the MME part. There is a separating key
between MME and BVE (2 pin positions).
This slot can be found only on machines, that do not supply an onboard
Base-Video system, like Models 76/77 (Bermuda-based), 85, and 95.
The machine's video card (XGA,
XGA-2 or SVGA)
plugs into this slot and is enabled to communicate with a card that sits in a
probable AVE slot. All sync signals, blanking, and pixel data are supplied over
this BVE connector.
On the XGA adapter the BVE connector is the short one to the rear the MME
part is left out. Therefore there is a large gap between the BVE part and the
rest of the MCA connector. If the XGA is set to boards with Base Video this BVE
part plugs nowhere and is just hanging free because systems with onboard video
don't have a BVE connector.
|