|
7677ref.exe Model 76/77 Reference Disk v3.10 (zipped image)
7677diag.exe Model 76/77 Diagnostics Disk v3.11 (zipped image)
7677flsh.exe 76/77 BIOS Revision Level 7 (Build 59A) (zipped image)
g7jt60a.exe 76/77 BIOS Revision Level 8 (Build 60A) (zipped image)
g7jt61a.exe 76/77 BIOS Revision Level 9 (Build 61A) (zipped image)
194-206 IBM PS/2 76 and 77 Family of Systems and Options (i/s)
7677dosd IBM Enhanced Local Bus DOS/Win 3.1 driver disk
S3 928 Windows 95 drivers disk
Win95-Setup for S3-928 From Peter Wendt's site
S3 86C928 GUI Accelerator (202 pages, datasheet/programming)
L2 Cache Modules
486 Interposers and Upgrades
DIY Lacuna VRM (from Alfred Arnold)
Sandy's "Cyrix and Lacuna" pages:
Part I |
Part II |
Part III
Lacuna Planar
Lacuna Versions
Lacuna Riser Cards
Flash BIOS Update Disk
BIOS Revisions
Can't Access System Partition
CPU Voltage
Installing a 5 V CPU (Jumper Setting)
Installing an 83 or 63 MHz POD
Installing a 3.45 V CPU
Voltage Regulator Module (VRM)
VRM Connector Pinout
VRM Circuit Diagram
VRM Hack
Interposer for POD
Dirty Secrets of the POD
IDE Devices
IDE Hard Drive
Large Hard Drives
IDE Capabilities
IDE Header
Boot Sequence
IDE CD-ROM
IDE CD-R Burner
IDE Zip Drive
Parallel Port
ECP Support
Direct Cable Connection under 95
"!" Under 95
Video
S3-928 Trivia
800x600x64k under W95
AVE Slot
Video Adapters under W95
Lacuna Video Glitch
MediaBurst Module
Cache Modules
Overclocking the Lacuna board
Early Lacuna Streaming Limitations
Speaker Noise
Lacuna Planar (76/77 i/s)
25 MHz: FRU P/N 95G9691 (bad, yellow U74) or 96G1305 (ok, blue U74)
33 MHz: FRU P/N 95G9692 (all ok, blue U74)
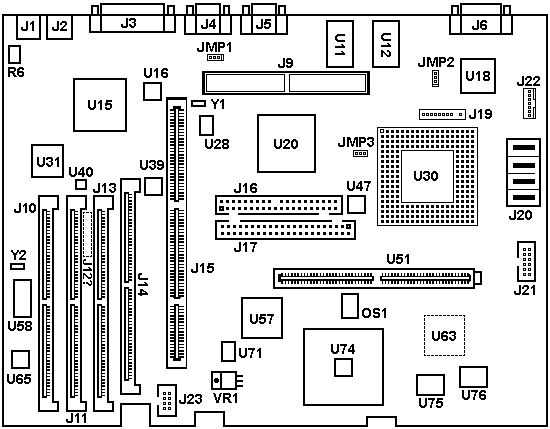
Important: The electrolytic capacitor in
position C68 is prone to leaking! If your
board is affected by this problem, you should replace the capacitor and clean
the affected area as soon as possible. Otherwise, the leaking electrolyte will
damage the nearby components, PCB traces, and vias!
The capacitor is 10 µF 25 V (d = 5 mm, l = ~5 mm).
JMP1 is the Power-On Password jumper.
The POP can be cleared by moving the jumper to the other set of pins, then
powering on. After power on, you can leave the jumper on the pins that you
moved it to.
JMP2 is the Privileged Access Password
jumper.
Locked State: jumper across middle pin - pin 1 PAP cannot be set, changed, or
removed.
Change State: jumper across pin 0 - middle pin PAP can be set, changed, or
removed.
My humble suggestion - DON'T SET THE PAP! If you
forget it, the planar is hosed.
VR1
LT1085CT Adjustable Voltage
Regulator with max. output current 3.0 A. The regulator is set to 3.56 V and
powers the System Controller (U74) and the unpopulated 486SLC3/BL2 (U63).
Supports 100 ns streaming data transfers between adapters. Planar devices
can use streaming only if L1 and L2 cache is in Write-Through mode!
Memory
RAM:
4 MB, 8 MB and 16 MB 70 ns SIMMs, Parity or ECC.
ROM:
256 KB (2 x 128 KB) Flash ROM
Cache:
L1: 8 KB (486SX/SX2/DX2), 16 KB (486DX4)
L2: Optional L2 cache module, 128 KB or 256 KB
Lacuna Versions
There were several versions of the "Lacuna" board:
- 95G9691 - 25 MHz only, yellow U74, not streaming transfer capable
- 96G1305 - 25 or 33 MHz, blue U74
- 95G9692 - 33 MHz, blue U74
Lacuna Riser Cards
Lacuna 76 Riser FRU 68G2706
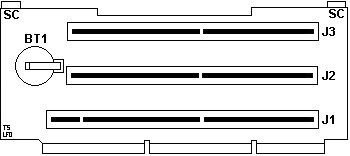
BT1 CR2032 Battery
J1 32-bit MCA slot with Auxiliary Video Extension (AVE)
J2, J3 32-bit MCA slots
SC Spring Clip that presses up against bus adapter support
Flash BIOS Update Disk
The 7677 FLASH Disk is for the Lacuna planar. Older Model 76 and 77 have the
Bermuda planar which does *not* have FLASH BIOS.
BIOS Revisions
Flash BIOS Revisions:
Level 03
Original release
Level 04
Contains the following enhancements:
- Third Party Video Adapter enhancements
A monitor attached to a 9576 or 9577 with a Cornerstone ImageAccel Adapter
displays a white screen during POST. This was fixed with Flash BIOS rev 04 on.
The terminator, shipped with the ImageAccel, must also be installed.
Level 05
Contains the following enhancements:
- Electronic eject floppy diskette drive compatibility
- Image/I Adapter/A compatibility
- Melco 1.44 floppy diskette drive compatibility
(Fixes 605 POST error with Melco floppy OEM'd for IBM, FRU P/N 85F0050.)
Level 07
Unknown.
Level 08:
Fixes "IRQ 00 Not Being Serviced" Errors In Error Log
BIOS Revision Notes & Experiences
Charles Lasitter:
So how did anyone figure that "8" was an improvement, other than
Y2K? I'm guessing that "4" would have worked after a manual reset.
Peter Wendt:
The later BIOS releases after 02 / 03 contain some few fixes for
the nasty Brooktree RAMDAC problems that cause checkerboard / yellow /
half-screen-black / speckled ASCII-garbage video errors under OS/2 and give
additional "over 524MB IDE support". Haven't read all the accompanying comments
:-)
Jim Shorney:
Hmm... Just checked. My Lacuna is Rev. 7, happily running a POD
83, write-back, no interposer. Guess I'll leave it at seven.
Can't Access System Partition on 76s (maybe others)
On the 76i / 77i with the Lacuna planar (and planar IDE, S3-928 SVGA) the
"system partition" is only for convenience - but it is not required for getting
parts of the BIOS into the memory as on the older 76 / 77 with the "Bermuda"
planar.
The 76i / 77i are "non-IML" machines and do not support a "real system
partition" anyway - they just offer the ability to "park" the reference and
diagnostic disk for easier access on the harddisk. Otherwise called a
Convenience partition.
Ed. But they DO support a Convenience Partition
IF you use an IBM SCSI adapter (NOT the FD SCSI-2 that is standard). To install
a Convenience Partition and be able to access it, you have to LLF the drive and
then restore the partition. Just running "Restore System Partition" without
LLFing the drive first will result in the system refusing to access the
partition. I have a Fast/Wide in my 77s, and I can bring up the Convenience
partition with F1. So much better when you have a huge pile of poorly titled or
untitled floppies on your desk...
However: I had similar problems getting a system partition on the drive.
There had been one once on your drive (the unused 4MB space) but it has been
loused up by what reason - same what happened to me. In this case the MBR of
this "hidden" partition is invalid and cannot be used any longer. Therefore
"Restore system partition" does not work. The only way to get it back is in
fact a Low-Level format. In fact the order is important.
You need to install the system partition first, *then* run FDISK from any
other operating system. Some FDISKs (like that from OS/2 2.x) do not always
accept the "system partition" as hidden... :-) ...and simply overwrite it or
corrupt the boot / MBR information. OS/2 2.1 CID installation was famed for
lousing up the system partition on the 76i / 77i.
My recommendation: If you already have a lot stuff on the drive - leave it
as it is. If you'd only installed the Win95 so far - mind running the LLFORMAT
and install a system partition. You need to start with the reference in A: and
press CTRL+A in the main menu to start (A)dvanced Diagnostic. Then run "Format
harddisk" and follow the instructions on the screen. Reboot after finish -
restart with the reference disk and run "Restore system partition". Worked fine
when I tried it last time...
CPU Voltage
Installing a 5 V CPU
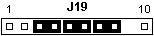
Jumper 3-4, 5-6, 7-8 (pin-9 = key, missing).
Installing an 83 or 63 MHz Pentium Overdrive Processor
Diags Level G7GT55A or higher and
interposer required. Jumpers in J19 must be set for a
5 V CPU (the POD has a built in 5 V to 3.45 V regulator)
Installing a 3.45 V CPU
Remove the jumpers. Install VRM.
VRM Connector Pinout
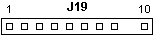
| Pin | Description |
|---|
| 1 | Presence Detect. / Sense? |
| 2 | Ground (GND) |
| 3, 5, 7 | VRM Input Voltage (5 V) |
| 4, 6, 8 | VRM Output Voltage (3.45 V) |
| 9 | Key / Missing |
| 10 | Not Connected |
Voltage Regulator Module (VRM) FRU 06H3011, ASM P/N 06H3010
The Voltage Regulator Module (VRM), made especially for the 9576/77i system
board. It is used to reduce the CPU core voltage from 5.0 V to 3.45 V. That
makes it possible to put an Intel 486DX4/100 or AMD 5x86/P75 CPU on the board
to upgrade the performance.
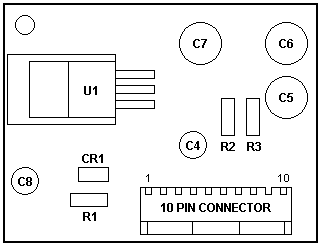
|
U1 LT1085CT Voltage Regulator
R1 1.5 kΩ 1/4 W 5% mf
R2 200 Ω 1/4 W 1% mf
R3 348 Ω 1/4 W 1% mf
CR1 1N4001
C4 10 uF 50 V 105 °C
C5 220 uF 16 V (25 V) 105 °C
C6 220 uF 16 V (25 V) 105 °C
C7 220 uF 16 V (25 V) 105 °C
C8 10 uF 50 V 105 °C
(mf - Metal film resistor)
|
VRM Circuit Diagram
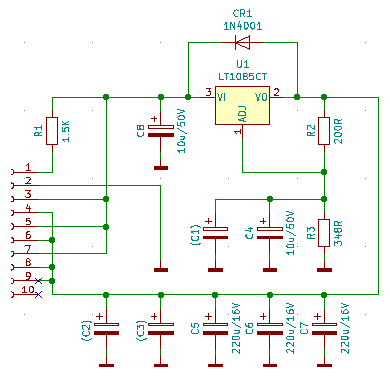
(Click on the picture for a hi-res version)
Ed. Tom: The original diagram by J. Shorney had
all the input and output pins swapped! This is now corrected (with some other
minor adjustments).
Jim Shorney says:
R2 and R3 should be 1% or better precision resistors, since
they set the output voltage of the regulator.
Note: Don't substitute a 'close' standard value
for R3. If you don't have access to the exact value; a 300 ohm resistor in
series with a 100 ohm trimpot could be substituted for R3 to allow fine trim of
the regulator voltage.
The formula for calculating the resistors is in the regulator
datasheet. Use the simpler
formula that ignores reference current.
VRM Hack
Alfred Arnold shared his experience.
Interposer for POD
Interposer is required to properly support L2 cache on a number of systems.
Sometimes, even an interposer isn't enough... 19x19 pin - PGA socket (top-view)
Push out the identified pin using a soldering iron.
(Ed. Tom: This will completely disable the
Write-Back cache mode as described down below.)
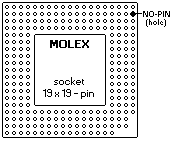
|
From Tam Thi Pham:
Tested out a custom home-brew interposer with the "missing" pin
as shown and lo and behold, I can now enable write-back caching on the 256K
cache module when run a Pentium 83 MHz Overdrive. Previously, I could use the
POD but only with the cache set to Write-Through.
|
Ed. Tom:
By removing pin T1 (WB/-WT) you are effectively forcing the processor into the
"standard bus" / Write-Through mode
(see HERE
for more info). So, even if the cache module can be set to WB with this
modification, the CPU will operate in WT mode only. I would strongly recommend
some proper benchmarking to see what configuration gives better performance.
Note: Some systems do NOT accept ANY (WB)
L2 cache modules. I have three Lacunas, none of them supported any of the IBM
marked modules or IDT modules. Other people (Bob Watts among others) just seem
to drop a POD in their machine, toss in any old L2 module, and it comes up happy.
It is NOT the fault of the interposer. Go
HERE for details.
Dirty Secrets of the POD (From Peter, edited)
The whole Pentium Overdrive debacle was a mess from the beginning, with
Intel changing specs and making motherboard manufacturer's and BIOS writers
crazy. (And Louis tried every BIOS level and revision I'm sure.)
In fact they changed the PODP specs shortly before announcement. This L2
communication problem shows up on all these machines where the design work
starts in early 1993. At IBM these are namely the PC-300 and the "Lacuna". In a
way the PODP was the Edsel of the processors: good idea, bad marketing - and
outdated in the right after announcement. Intel hurried it a bit - when the
problems showed up the major work was already done for the board-makers.
The main reason for this (AFAIK) is that the original concept did not
include boards with L2 WB-cache... the most of the older boards did not have L2
- and if, then it were simple WT-cache. <snip>
Method for Interrupt Sharing with IDE Hard Files in IBM PS/2 Systems
From IBM Technical Disclosure Bulletin (June 1994) (priorart.ip.com)
Disclosed is a method that allows the interrupt request of an IDE hardfile
to be shared with another device (e.g., SCSI hardfile) on interrupt level 14
within an IBM PS/2* system.
The interrupt request (IRQ) of an IDE interface was designed to be on a
non-shared interrupt level. According to PS/2 Micro Channel* system
architecture, all hardfile IRQs are shared on interrupt level 14. In a Micro
Channel computer system that supports both an IDE hardfile and a SCSI hardfile,
a problem arises. The essence of the problem is that because the IDE interface
IRQ was designed to be non-sharing, no IRQ "indicator bit" exists in any of the
IDE status registers. In order for interrupt handling software to determine
which of two or more devices sharing an IRQ level is the requesting device, an
IRQ "indicator bit" or status bit is needed. The Figure shows a simple solution
to provide the IRQ "indicator bit".
To provide the IRQ "indicator bit" for the Micro Channel IDE interface, bit
2 of port 92 was selected. In previous systems bit 2 (port 92) was connected to
a pin in the I/O controller chip called SECURITY OVERRIDE. SECURITY OVERRIDE is
a signal that can be mechanically jumpered to ground by a customer engineer to
override and reset the system password. It sets port 92 bit 2 which is read by
POST during system power-up initialization. In normal functional operation,
SECURITY OVERRIDE is a static signal tied to +5V. Because SECURITY OVERRIDE
will only be jumpered to ground in the unlikely and infrequent case of a
customer engineer making a repair to a PS/2 system, bit 2 of port 92 is
multiplexed to monitor the IDE IRQ14 line and serve as the needed "indicator
bit" as shown in the Figure. The enable for the multiplexer is bit 4 of port E3
which is an output (ROM_PAGE) from the memory controller. During POST
initialization, bit 4 of port E3 is set to 0, and the SECURITY OVERRIDE signal
is selected and its polarity can be read from bit 2 of port 92. After the
necessary testing and initializations have been done, bit 4 in port E3 is set
to a 1 before exiting POST. IDE IRQ14 is then selected through the mux shown in
the Figure and latched with a free-running clock into bit 2 of port 92. Bit 2
of port 92 then functions as the IDE IRQ "indicator bit".
IDE Hard Drive
I used these to run a WD2540 in 32 bit mode Same as
above, Manual installation.
Standard IDE/ESDI HD Controller
IO Range 01F0-01F7
IO Range 03F6-03F6
IRQ 14
Though others have successfully used the Busmaster IDE HD controller. When I
set up the 540, it was for an ISA/PCI machine with built-in IDE controller. I
was looking for as much compatibility as possible.
Large Hard Drives
From Michael Lybarger:
I just installed a Maxtor 10.2 gig "Diamondmax" 7200 rpm unit on
my 77s and upgraded to win 98 (from 95). I could not get the hard drive, CD-ROM
or floppy drive (!) to run with a protected mode driver, as they did with my
previous configuration (using 2 SCSI 270 MB drives instead of the big IDE and
one SCSI I have now).
First I tried to use FDISK, (the latest version, that supports 32 bit), but
it would not allow me a partition bigger than 7.23 gig or something like that.
I do not know the reason for this. Anyway, the max blast program worked great-
I got the whole 10.2 gig (which was the primary reason for going to win98
anyway- 95a does not support a 32 bit FAT). As I said, once I got it set up
properly on IRQ 14, It ran in protected mode with the windows driver.
From Ron Doran:
I have recently had great success with on 850MB Western Digital
IDE drive on the connector with no formatting problems, but the machine puked
when I tried 2 different 1024MB Seagate drives on it. (puked=low level format)
;)
From Peter:
If you have a BIOS revision 07 or 08 even if you have a drive over
4GB you don't need a disk-manager... you only cannot install a convenience
partition on that drive. My 9577-BTG has a 4.51 GB Seagate Barracuda installed.
Works fine - but I have to fiddle around with the ref and diags floppies once I
change something.
IDE Controller Capabilities
The on-board IDE is a "single channel" IDE but rumors say BIOS 08 is capable
to handle drives over 528 MB, mine at home currently runs with a 650 MB, so it
is in a way a "half EIDE" interface. Pretty strange.
IDE Planar Header (Where's pin 1?)
Based on personal experience, the IDE header on the Lacuna planar uses a
polarized plug. BUT look at the header- it uses TWO keys, one near each end. If
you have the common IDE polarized plug on your cable, it has ONE centrally
located key...
Luckily, I found a non-polarized plug (no keys at all). All you ISA/PCI
veterans know what to do if the system refuses to boot -
check the cable pin 1. (I just turned the cable 180,
plugged it in, and it booted.)
If you do not have the uncommon dual key plug, simply use a file or a sharp
knife and remove the polarizing key off an IDE cable you have laying around.
Note that Pin 1 is toward the riser! Look at the planar illustration. The red
marked wire goes toward the riser!
From Dr. Jim:
If an IDE data cable is plugged in backwards, it can hold the
reset line on the motherboard down. The result is a motherboard that appears
dead.
From Martin Adams:
I tried to install an IDE CD drive. I had read all the stuff on
Louis page on installing a IDE CD. And reviewed all of Bob Watts notes, looked
very easy. I had a cable with out any external key so it would fit in the weird
double keyed socket. (Ed. Look directly above this
paragraph!)
I had the drive set as master, but what ever I did, 3 different cables 3
different IDE CD's. Another planner. Nothing would work. Damn drive door
wouldn't even open.
I was looking at the planner and it hit me. I had assumed that pin 1 for the
IDE port was on the same end as the FDD cable. I noticed one of the middle pins
that was cut for use of a cable the was plugged to act as a key.
I had been hooking up the cable on the planer backwards all the time!
So note pin one for the IDE is towards the riser card.
Boot Sequence
The "Lacuna" board has a 40-pin single-channel IDE controller port just
above the FDD-port. It nicely takes harddisks over 524MB if the Flash BIOS
release is 08 or 09 (G7GT61A).
The IDE-channel accepts two devices in the usual master / slave
configuration on a standard IDE-cable. There is however some care required if
you want to use it simultaneously with the SCSI adapter. You need to set the
boot-sequence in the "features" properly - to avoid problems when the system
tries to boot from an IDE CD-ROM... :-)
IDE CD-ROM on 76/77 i/s
I recently bought an IDE CD-ROM for a 9577 (VTG). I connected it on the
motherboard IDE controller. It works correctly under DOS with the following
commands:
CONFIG.SYS:
DEVICE=BTCDROM.SYS /D:MSCD001
AUTOEXEC.BAT:
C:\WINDOWS\COMMAND\MSCDEX.EXE /D:MSCD001 /V
But when I try to start Windows 95, everything STOP during initialization of
Windows.
Morten Kristensen:
You have to manually install an IDE driver in Win95. Control Panel
-> Add New Hardware. Do not let Windows find it automatically! Add an
Standard IDE/ESDI Harddisk Controller, IRQ=14, I/O=0x170 (maybe it is 0x1F0).
Now you are able to use the CD-ROM without DOS drivers.
IDE CD-R Burner
I have the IDE version of the Model 9576. I want to add an IDE based
CD-Reader Writer BUT can't get the reference program to recognize the fact that
something is there.
Peter responds:
Uhm, do you still use the IDE port for a harddisk ? If so: check
if the harddisk requires a particular jumpering for "Master with a Slave".
"Single Drive" should be avoided consequently :-)
If you don't have a HD on the IDE port: jumper the CD-burner as "Master".
The IDE port often dislikes the use of a "Slave only" configuration. And check
your systems' BIOS level. Those before 07 had several limitations on the type
of supported devices / drive sizes. Take 08 at least.
IDE ZIP + Lacuna
From Bob Watts:
Since the Iomega ZIP drive is an ATAPI compliant device, I was
pretty sure it would work, but you never know. I simply plugged it into my IDE
cable, and Windows 95 OSR2 found it and installed it instantly with no
problem.
For further information, an IDE CD-ROM device was previously on this cable,
and it is jumpered as Master, and the ZIP drive is jumpered as Slave. Also, an
IBM 0662 1 gig SCSI drive is the boot drive, on the factory installed Future
Domain controller.
Video
S3 928 Video Drivers
S3 and Diamond merged, lookit
HERE.
S3-928 Trivia (from Peter)
The S3-928 version used in the Lacuna contains a "special" IBM video
BIOS that includes all XGA-2 modes to allow the use of 951x monitors with that
machine. The S3-928 cannot be disabled physically. It goes in some sort of "sleep
mode" when another VGA / SVGA capable card is detected - nonetheless parts of
the card is still activated and *may* cause trouble.
Not confirmed: the early BIOS releases below 07 seem to be more vulnerable
to video disturbances with S3 and other video cards. One thing IBM tried to fix
with 07. In either case you better use a BIOS 08 - also for the "over 524MB HD"
capability. The XGA-2 card has not been announced to be used with the "Lacuna"
series anyway. IBM seems to have removed the card from the list, because in the
first announcement of the 76i / 77i the XGA-2 is still listed - not in the
later product / option matrices and product descriptions on the
"Lacuna". The 9515 and 9517 monitors are not 800 x 600 capable *per IBM*. They can
be tweaked to show an 800 x 600 like picture, but it is distorted and the
monitors have no explicit mode for it. These screens are "XGA-2 only"
Multi-Mode screens with fixed adjusted presets. They are no Multisyncs.
If you want to run the Lacuna with most of the possible modes switch to a
9525 or 9527 monitor. Or any other good SVGA screen. I run my "workhorse"
9595-S30 with XGA-2 on an Eizo F35, the 9577-BTG runs with a NEC 15XE and both
do fine. Nonetheless the XGA-2 (at least) will run in a Lacuna. There might be
some interference to clear out manually during OS installs, which is the
primary video system. This is usually the one with the monitor attached. In 99%
of all cases OS'es get that right - but sometimes the on-board video is ranked
higher and the OS gets confused. (Haven't seen that too often to be true - but
can happen).
800x640x64k under W95
The onboard video chipset is a S3-928 SVGA. The box runs nicely with Win 95
- will most likely also run nice with Win98, since it has IDE and not IBM MCA
SCSI (which is only merely supported with 98). To install the appropriate
drivers for DOS/Win 3.x / Win95 see the "W95
Setup for S3 SVGA" setup page. This will enable your machine to use the
full potential of the S3 chipset.
AVE Slot
Display adapter cards that use the Auxiliary Video Extension when installed
in a system require installation in slot one (9576) or slot two (9577) and
attachment of a display to the system video connector during configuration of
the system.
Video Adapters under W95
There is no way I know of disabling the on-board video. W95 says there is a
conflict, but none shows up under Device Mangler. You cannot successfully
configure the add-in video card.
Lacuna Video Glitch
> I have a 77s that has displayed a charming quirk- it waves the top half
inch of the screen. Not all the time, but...
Please check the type of the Video RAMDAC - and the origin of the S3 chip.
Some Thailand-S3s have internal bugs using an earlier stepping mask. The RamDac
should be the AT&T in this case. These were the machines that cause massive
faults under OS/2 2.1...
The S3 chips are famed for a lot "undocumented features" (like using an
address for COM4 (? yes - think so)) and this chipset is -basically- a VESA
Local Bus chipset which is stitched in the Lacuna planar with a hot needle.
> IIRC, the last three digits of one of the S3's I/O ports is 2e8. Like
B2e8h or something
Yep. That was it.
> If I understand this correctly, it wasn't S3's fault that some com port
hardware did faulty address decoding.
Yes and No. On MCA it wouldn't have been too bad, because MCA *should* use a
full decoding (or: 24 bits at least, 16 bit for the I/O range), but -again- the
VLB chipset was a little buggy already, before IBM decided to put that on a MCA
platform. Who's to blame ? S3 -in addition- delivered chipsets which were out
of specs for some series which made things worse than it already was.
> The workaround was to not use com4/2e8 if possible, or to remap com4 to
a different address if it was really needed.
IBM's COM3 - 4 ports on the PS/2 were not "XT-style" so this COM/Video
interference wasn't much of a problem here. It was *much* worse on the "Rocket"
PS/VP Series 3, which were PCI/ISA with more generic layout and addresses. They
used S3 chipsets too...
> I have seen Lacunas with S3-928 Rev. G and Rev. P. Seen both kind with
either a BT or AT&T DAC also.
Most likely the -G- revisions are afflicted by what IBM euphemistically
called "video timing glitch"... which cause the entire machine to crash under
OS/2. IBM offered various bug-fixes for OS/2 2.1 and tried to fix the problem
with modified hardware as well, which lead to slight incompatibilities with
driver versions. The drivers for the original (un-fixed) 2.1 did not work very
well with these machines. The APARs offered for Germany were... now... not so
good. The US-APARs seem to be better, but you should not mix different language
versions within any OS. The later series of the "Lacuna" seemed to be more
stable and especially with OS/2 Warp the problems rarely occurred.
Some machines that have been migrated to Win95 show up odd effects recently.
Especially when switching to and from DOS-boxes into full-screen hi-res modes
may cause the system to hang, fall into GPF or show odd colored icons / missing
icons / speckled screen etc. This seems to be caused by a faulty, out-of-time
palette read... haven't noticed that on my machine, so I guess the -P- level of
the S3 seems to be stabilized.
MediaBurst Module FRU 82G4884
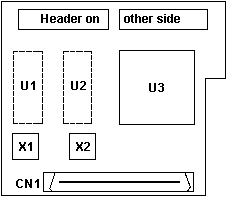
|
mediabst.exe DOS/Windows drivers
mediaos2.exe OS/2 2.11 drivers
mediaos2.txt readme for Mediaos2.exe
CN1 Male 68 pin VMB
U1, U2 Solder pads
U3 Vialogic VL i110 A (PowerPlay 32)
X1 32.000 MHz
X2 25.000 MHz
|
MediaBurst Movie Adapter expands up to four times the window size of many
software motion-video compression algorithms, such as Video for Windows or
Ultimotion(TM), and provides access to the VESA Media Channel (VMC)
The MediaBurst Movie device driver uses the PowerPlay 32 video
accelerator chip to provide enhanced playback of digital video. This allows
viewing of video clips in larger-sized windows or full-screen without the
degradation in speed and picture quality usually associated with software
motion video.
Key features of the MediaBurst Movie option include:
- Full-screen video at up to 30 frames per second (fps)
- Smooth scaling of the video image for better picture quality
- Support for IBM OS/2 MMPM/2 and Microsoft Video for Windows movie formats:
- INDEO 2.1, 3.1
- Ultimotion
- Audio Video Interleave (AVI)
Resolution Supported By Mediaburst Option:
Graphics AVI File Video Smooth
Mode Colors Format Acceleration Scaling
-------------------------------------------------
16 ALL No No
256 8-bit Yes No
palletized
256 All Others No No
64K All Yes Yes
16M All No No
My thanks to Brad Parker for ripping apart his 77s and
sending me a scan.
Parallel Port
ECP Support
Does the 77i even support ECP? My printer/CD/ZIP drive
doesn't work...
From Peter:
Do the following:
- boot into reference (either disk or system partition if one installed)
- enter "Set configuration"
- find the "Parallel Port DMA" and set it to "Disable".
- press [F10] to store the config... [F3]/[F3] to leave.
That should fix the problem. The 9577 -as most PS/2- has a "DMA-arbitrated"
LPT-port, which is neither ECP nor EPP, only "sort of". The "Disable" directs
the machine not to use DMA during bi-directional transfers and use a contiguous
data-stream.
The DMA-mode tends to miss returning signals from PP-devices especially PP
CD-ROMs, Tapes and Zip-Drives. Some printer-drivers use the bi-directional
communication to signal details from the printer back to the computer.
Direct Connection under W95
Yes it does work. I even used the ECP port
setting with the parallel cable. Both ports were at
Parallel 2, and DMA Arbitration 1.
For a detailed description of the DCC process,
95 to 95, 95 to 3.1x, etc. check out
Connect Pages at Kime.Net
(dead, archived copy).
Parallel Port "!" under W95 with Audiovation
I was thinking way too hard on this. The default choice for W95 to assign an
IO Range for a MCA parallel port is 3BC-3BE. BUT this conflicts with the first
memory range of the S3 928 (check resources, the first range is 3B00-3BFF). Set
your parallel port to "parallel 2" under system programs, which is the standard
378-37D address. Then under W9x, set the IO range to 378-37A. "!" goes
away.
Overclocking the Lacuna board
From Zp Gu:
This mod is relatively easy. I changed the 66.667 MHz osc to an 80
MHz surface mount crystal osc. from Digikey and the board is now running an
AMD-133 at 160 MHz without any problem.
The board actually has 4 thru-holes under the osc, but IBM chose to put an
SMD instead of a half size socket. Socket would have made life much easier. I
didn't attempt to put a socket there since I don't have the right
equipment/skill to do so. I just soldered a surface mount 80 MHz to its
place.
Putting a POD83 in failed POST. I can't imagine Intel being so tight on
this, but maybe it's just my bad luck. Running it at 83 MHz was no problem.
From Peter Wendt:
My 9577-BTG chokes at power on with a 2401 "platform video error".
Obviously my S3-928 chipset dislikes the 40 MHz base clock. On attempting to
bypass the error with [F1] - "Start operating system" the system hangs with a
GPF-screen at Win95 logon ... or rebooted after the network adapter tried to
insert into the TR-network.
The effect was much worse with the Kingston Turbochip - but also noticeable
with the original DX4-100... where in addition the VRM turned really hot !
Significantly hotter than under normal operation - a sign that the power drawn
from the DX4 at 40 MHz is "a little bit" higher than at 33 MHz.
I had only a "full size" oscillator and needed to build a sort of "adapter"
from half-size holes to full-size socket. But that's a minor problem. *Then* I
needed to solder an adapter for the original 66.6667 MHz SMD-crystal...
Aaak!
Anyone tried that modification with a "Bermuda" ? These have MCA XGA-2 cards
and no "local bus video" as the "Lacuna". Should work a bit better there...
probably.
From Zp Gu:
This is definitely another warning to anyone who contemplates the
mod. You can't apply enough disclaimers to this kind soldering. Mine has no
VRM, originally DX2/66 with ATT20C490-11 DAC. The cache module feels very warm.
But then again, it's always very hot to the touch. I believe you can't set
Kingston TurboChip's level-1 cache to WB, hence it's the most compatible
upgrade (and least performing).
From Peter Wendt:
Mine has the Brooktree Bt495 RAMDAC... the cache module is the IDT
256K WT/WB with the IBM decals (tested in both modes and without - no change).
It already gets really hot during operation - even with the standard
486DX4.
Early Lacuna Streaming Limitations
(source)
LANStreamer and EtherStreamer adapters don't work in 76i/77i with 25 MHz
planar (FRU P/N 95G9691).
Streaming mode adapter cards are not supported for use with 76i/77i systems
fitted with 25 MHz planar. The problem is caused by a limitation of the level
of Bus Interface Controller chip used on this planar. Replace the systemboard
FRU P/N 95G9691 with FRU P/N 96G1305. (Identification - 95G9691 = 'yellow' /
96G1305 = 'blue' "SynchroStream Controller".)
Speaker Noise
From Peter:
When the Lacunas came out there was a series of falsely wired
"speaker /power switch / LED" units - which had the speaker wired to +5 V DC of
the HD activity LED instead to GND. Now - these machines made a lot noise when
accessing the harddisk :-)
|